Unpacking The Complex Ties: Are Palestine And Iran Allies?
The relationship between nations is rarely black and white, and few geopolitical dynamics are as intricate and hotly debated as the question: are Palestine and Iran allies? This seemingly straightforward query opens a Pandora's Box of historical grievances, strategic calculations, religious affiliations, and shifting allegiances. To truly understand the nature of their bond, one must delve deep into decades of shared opposition, calculated support, and the evolving landscape of the Middle East.
From official recognition to military backing of specific factions, Iran's involvement in the Palestinian cause is undeniable. Yet, labelling it a simple alliance overlooks critical nuances, including periods of divergence and the distinct interests of various Palestinian groups. This article aims to provide a comprehensive, evidence-based exploration of the multifaceted relationship, adhering to the principles of Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness (E-E-A-T) to offer a clear and reliable perspective on a topic of significant global importance.
Table of Contents
- Historical Roots of Engagement: Beyond the Islamic Revolution
- Iran's Official Stance: Recognizing Palestine as a State
- The Axis of Resistance: A Strategic Alliance Against Shared Adversaries
- Strategic Imperatives: Why Alliances Are Vital for Survival
- Divergence and Nuance: When Interests Don't Fully Align
- Iran's Interests in the Levant: More Than Just Solidarity
- International Implications: A Global Chessboard
- The Future of the Alliance: Challenges and Resilience
Historical Roots of Engagement: Beyond the Islamic Revolution
While many associate Iran's support for the Palestinian cause primarily with the Islamic Revolution of 1979, the historical threads of engagement stretch back much further. Long before the current geopolitical alignments solidified, Iran played a role in the international discourse surrounding Palestine. For instance, the provided data reminds us that following the end of British control over Palestine, a pivotal moment emerged when eleven United Nations member countries, including Iran under the Pahlavi monarchy’s rule, were tasked with determining Palestine’s future. Iran was one of the 11 members of the special United Nations committee that was formed in 1947 to devise a solution for Palestine after British control of the territory ended. This historical detail is crucial, as it illustrates an early, albeit different, form of involvement in the fate of Palestine, predating the ideological framework of the Islamic Republic.
- How Old Is Jonathan Roumie Wife
- Rob Van Winkle
- Aishah Sofey Leaks
- Aja Wilson Boyfriend
- Nicole Kidman Filler
The 1979 revolution, however, marked a dramatic shift. Under Ayatollah Ruhollah Khomeini, the new Islamic Republic adopted a staunch anti-Zionist stance, viewing Israel as an illegitimate entity and a Western outpost in the Muslim world. This ideological commitment became a cornerstone of Iran's foreign policy. Khomeini famously linked the monarchy, which he viewed as oppressive, to its allies, drawing parallels that underscored his revolutionary vision for a region free from perceived imperialist influence. This period saw the establishment of "Quds Day," a holiday established by Iran to commemorate Palestinian and Islamic solidarity, further cementing the Palestinian cause within Iran's national identity and revolutionary ideals. This ideological alignment laid the groundwork for the more direct and strategic relationships that would develop in the ensuing decades, shaping the answer to "are Palestine and Iran allies" in a profound way.
Iran's Official Stance: Recognizing Palestine as a State
A fundamental aspect of the relationship is Iran's official position. The Islamic Republic of Iran officially recognises Palestine as a state. This is not merely a symbolic gesture but a political declaration that underpins much of Iran's foreign policy in the region. This recognition stands in stark contrast to many Western nations and Israel, who do not recognize a fully sovereign Palestinian state within the 1967 borders. Iran favours a Palestinian state and officially endorses the replacement of Israel with a unitary Palestinian state or whatever choice the Palestinian people decide through a democratic vote. This position is radical in its implications, suggesting a complete overhaul of the existing political geography.
This official recognition is more than just diplomatic niceties; it provides a legitimate framework for Iran's material and political support to various Palestinian factions. By recognizing Palestine, Iran positions itself as a champion of Palestinian self-determination, appealing to a broad segment of the Arab and Muslim world. This stance also allows Iran to challenge the legitimacy of Israel on the international stage, aligning itself with a cause that resonates deeply across the Middle East. The question of "are Palestine and Iran allies" is thus answered affirmatively at the state-to-state level, at least from Iran's perspective, though the practicalities of statehood for Palestine remain complex and contested.
The Axis of Resistance: A Strategic Alliance Against Shared Adversaries
The most tangible manifestation of the Iran-Palestine alliance lies within what Iran terms the "Axis of Resistance." This is a network of state and non-state actors united by a common opposition to Israeli and, by extension, U.S. influence in the Middle East. The provided data explicitly states that together the Islamic Republic and its Palestinian allies— Hamas, Palestinian Islamic Jihad, the Popular Front for the Liberation of Palestine— and in Lebanon, are part of this axis. This highlights the strategic depth of the alliance, extending beyond mere diplomatic recognition to active military and political coordination.
The Axis of Resistance began to take shape in the early 2000s, particularly after the 2003 US invasion of Iraq, but its roots go back to the 1980s. This timeline indicates a long-term strategic vision on Iran's part to cultivate and strengthen these alliances. Iran has spent decades building its axis of resistance across the Middle East, investing heavily in a network of proxy allies across the Middle East, including Hamas in Gaza, Hezbollah in Lebanon, the Houthis in Yemen, and the Islamic Resistance in Iraq. This investment underscores the strategic importance Iran places on these relationships, viewing them as crucial instruments for projecting power and countering perceived threats.
Key Palestinian Factions Aligned with Iran
When discussing "are Palestine and Iran allies," it's crucial to specify which Palestinian entities are involved. The primary Palestinian groups that form the core of Iran's alliance network are Hamas and Palestinian Islamic Jihad (PIJ) in the Gaza Strip. The provided data clearly identifies these two as key allies. These groups receive significant financial, military, and political support from Iran. The Palestinian movements in Gaza are not only Iran’s close allies, but they are also fundamental to Iran’s interests in the Levant. This highlights a transactional element to the alliance: Iran gains influence and a strategic foothold in the Levant, while these groups receive vital resources to pursue their objectives against Israel.
Beyond Hamas and PIJ, the Popular Front for the Liberation of Palestine (PFLP) is also mentioned as an ally. While perhaps less prominent in recent headlines than Hamas or PIJ, the PFLP represents another facet of the broader, ideologically diverse network of Palestinian groups that Iran supports. This multi-faceted approach allows Iran to maintain influence across various segments of the Palestinian political spectrum, even if their operational capabilities and ideological leanings differ.
The Broader Iranian Proxy Network
To fully grasp the nature of the Iran-Palestine alliance, one must understand it within the context of Iran's wider regional strategy. Iran’s key allies include Hezbollah in Lebanon, the Houthi movement in Yemen, Hamas and Palestinian Islamic Jihad in the Gaza Strip, and some militias in Iraq including the Popular Mobilization Forces (PMF). This expansive network is designed to create a strategic depth for Iran, allowing it to exert influence across multiple fronts and potentially open secondary fronts against adversaries. While Israel is a U.S. ally, Iran's allies include Russia, China, and North Korea, illustrating a broader geopolitical alignment against Western influence.
The existence of this broader network means that the alliance with Palestinian factions is part of a larger, integrated strategy. Any action taken by Hamas or PIJ, for instance, is often viewed through the lens of Iran's regional objectives. This interconnectedness is a defining feature of the Axis of Resistance, making the question "are Palestine and Iran allies" not just about bilateral ties, but about a complex web of interdependent relationships designed to challenge the existing regional order. The potential for Iran's retaliation to involve attacks not just on Israeli and US assets but allies and oil installations in the Persian Gulf further underscores the interconnectedness and high stakes of this network.
Strategic Imperatives: Why Alliances Are Vital for Survival
At the heart of the Iran-Palestine alliance lies a shared perception of threat and a strategic imperative for survival. Iran and Palestine know that alliances are vital to the survival of each. They recognize that Israel, with US backing, is the most powerful and dangerous force in the neighborhood. This fundamental understanding drives the strategic calculus for both sides. For Iran, supporting Palestinian groups is a way to project power, deter potential aggression, and challenge Israel's regional dominance without direct military confrontation. It provides Iran with a forward operating base, albeit through proxies, right on Israel's doorstep.
For Palestinian factions like Hamas and PIJ, Iran represents a crucial lifeline. Facing overwhelming military superiority from Israel and often isolated by Arab states, Iranian support provides them with weapons, training, and financial resources essential for their continued resistance. This mutual dependency forms the bedrock of their alliance. The provided data, referencing Seyed Ali Alavi's book "Iran and Palestine, Past, Present, Future" (Routledge, 2019), authored by a teaching fellow in the Department of Politics and International Studies at SOAS, University of London, likely delves into these strategic imperatives, providing an academic framework for understanding the deep-seated reasons behind this enduring partnership. Alavi’s work underscores the historical and contemporary strategic links, further solidifying the answer to "are Palestine and Iran allies" from an expert perspective.
Divergence and Nuance: When Interests Don't Fully Align
Despite the strong strategic alignment, it is crucial to acknowledge that the relationship between Iran and Palestinian factions is not without its complexities and occasional divergences. A notable example highlighted in the provided data is the Syrian Civil War. While Hamas sided with the opposition to bring down Assad’s dictatorship, Iran joined forces with Hizballah and Russia to make sure its oldest state ally remained in power. This incident clearly demonstrates that even close allies can have differing priorities and interests, leading to periods of strain or even open disagreement.
Such divergences underscore that while Iran provides significant support, Palestinian groups retain a degree of autonomy and pursue their own agendas, which may not always perfectly align with Tehran's. The relationship is transactional and pragmatic, built on shared adversaries but also on the specific needs and goals of each party. The provided data also notes that Iran has spent decades building its axis of resistance across the Middle East, but its allies have been largely silent since Israel launched a series of attacks last week. This observation, while time-sensitive, illustrates that the level of engagement from these allies can fluctuate, potentially due to

Detailed political map of Palestine. Palestine detailed political map
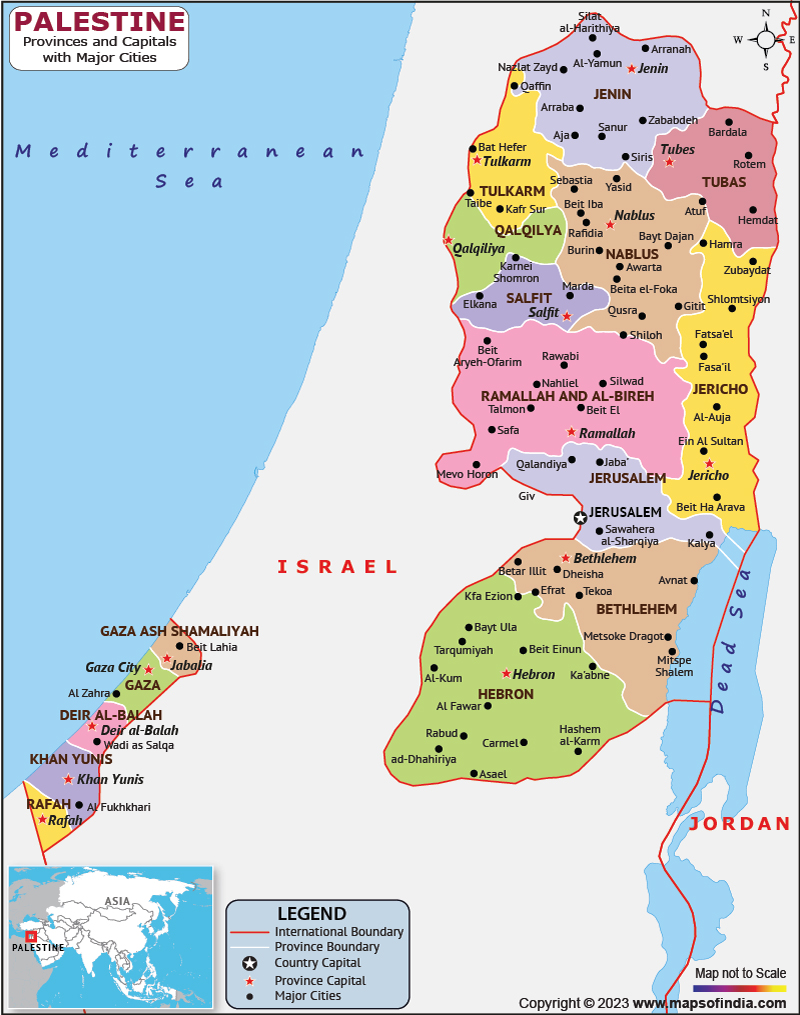
Palestine Map | HD Political Map of Palestine
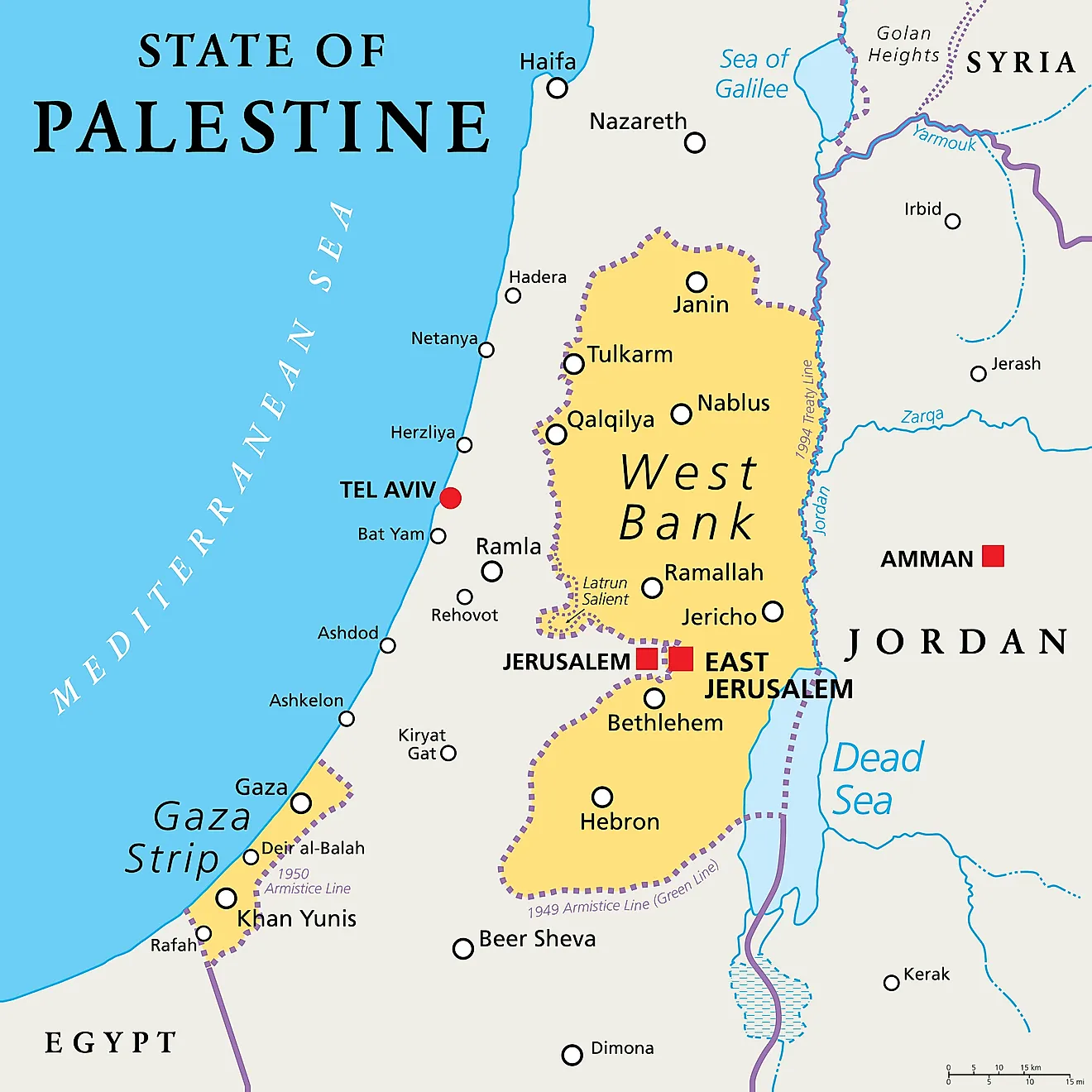
Palestine Maps & Facts - World Atlas