Decoding Iran's Population Density: Trends, Challenges, And Future
Understanding the intricate dynamics of population density in Iran is crucial for comprehending the nation's demographic landscape and its implications for development, resource management, and urban planning. This article delves into the fascinating patterns of how people are distributed across this vast and diverse country, exploring the nuances that shape its demographic present and future.
From historical shifts to future projections, we will explore the key factors influencing Iran's population density, examining its current state, the significant role of urbanization, and the unique challenges and opportunities that arise from these demographic realities. By analyzing available data and trends, we aim to provide a comprehensive overview that sheds light on one of the most fundamental aspects of Iran's societal structure.
Table of Contents
- What is Population Density? Defining the Metric
- Iran's Current Population Density in Global Context
- Historical Shifts in Iran's Population Density
- The Urbanization Phenomenon and Its Impact on Density
- Factors Influencing Iran's Population Dynamics
- Regional Disparities in Population Density Across Iran
- Future Projections and What They Mean for Iran's Population Density
- Navigating the Challenges and Opportunities of Density
What is Population Density? Defining the Metric
At its core, population density is a straightforward yet powerful demographic metric. It measures how many people live per square kilometer, effectively showing how a population is distributed across a given area. This calculation is typically derived by dividing the midyear population by the total land area in square kilometers. It's important to note that the "total area" often includes both land and water areas within a country's international boundaries and coastlines, providing a comprehensive spatial context for the population count.
Understanding population density goes beyond mere numbers; it offers critical insights into a nation's resource allocation, infrastructure demands, and urban planning needs. High population density in certain areas can indicate concentrated economic activity, but also potential strain on public services, housing, and environmental resources. Conversely, low density might point to vast undeveloped regions or areas facing out-migration. For a country like Iran, with its diverse geography ranging from arid deserts to fertile plains and mountainous regions, analyzing population density is key to understanding its unique developmental trajectory and the challenges inherent in managing its human geography.
Iran's Current Population Density in Global Context
When we examine Iran's current demographic standing, its population density offers a compelling snapshot. As of recent estimations, the current population density of Iran (Islamic Republic of) stands at approximately 56.7415 people per square kilometer. This figure is a slight increase from 56.2196 people/km² in 2024, reflecting ongoing, albeit moderate, population growth. Looking ahead, the 2025 population density in Iran is projected to be around 57 people per km² (147 people per mi²).
To put this into perspective, Iran's total land area is a vast 1,628,550 km² (or 628,786 sq mi). This expansive territory, combined with its population, positions Iran distinctly on the global stage. Iran's population is equivalent to 1.12% of the total world population, making it a significant demographic player. In terms of overall population size, Iran ranks number 17 in the list of countries (and dependencies) by population. However, when considering population density per unit area, Iran ranks 21st in the world. This distinction highlights that while Iran has a substantial population, its vast landmass means that its density is not as high as some smaller, more densely packed nations, yet it is still a significant factor in its internal dynamics.
Historical Shifts in Iran's Population Density
The story of Iran's population density is one of profound transformation over the past century. Looking back, the country has experienced a remarkable surge in its demographic footprint. From 1880 till 1920, the population of Iran remained relatively stable at 10 million or below. However, from 1920 onwards, it began to increase steadily, reaching 20 million by 1955. This initial growth laid the groundwork for the more rapid changes that would follow.
The shift in population density is particularly striking when viewed across several decades. In 1950, the country's density was a mere 10.1369 people/km². Fast forward to 1980, and the population density of Iran had risen to 23.7. By 2023, this figure had more than doubled to 52.6 people/km². The 2024 density of 56.2196 people/km² further underscores this continuous upward trend. These figures illustrate a nation that has undergone significant demographic expansion, driven by factors such as improved healthcare, higher birth rates in earlier decades, and evolving socio-economic conditions. This historical trajectory provides crucial context for understanding the current challenges and opportunities associated with population distribution in Iran.
The Urbanization Phenomenon and Its Impact on Density
One of the most defining characteristics of Iran's demographic evolution has been its rapid urbanization. This shift from rural to urban living has profoundly impacted the nation's population density, concentrating a significant portion of its inhabitants into a relatively smaller geographic footprint within cities. The statistics clearly illustrate this trend: urban population has increased dramatically from 42,352,162 people (representing 64.0% of the total population) in 2000 to an estimated 67,435,000 people (or 77.8%) in the current year. This substantial migration to urban centers has led to a noticeable increase in population density within these areas, even as the national average may seem moderate due to vast unpopulated regions.
This rapid urbanization presents both opportunities and challenges. Cities become economic engines, centers of innovation, and hubs for service delivery. However, they also face immense pressure on infrastructure, housing, and environmental resources. The concentration of people in urban areas necessitates careful planning for housing construction, transportation networks, and utility provision. The article highlights that the main objective factors affecting the development of housing construction in Iran are directly linked to this urban growth, as authorities strive to accommodate the increasing number of city dwellers and manage the escalating population density within urban boundaries.
Tehran: A Case Study in Urban Density
Nowhere is the impact of urbanization on population density more evident than in Iran's capital, Tehran. With around 10 million people residing within its nearly 300 square miles, according to the C.I.A. World Factbook, Tehran is a megacity whose density is comparable to that of New York City. This staggering concentration means that approximately one in 10 Iranians lives in Tehran, making it the undeniable demographic and economic heart of the country.
The sheer scale of Tehran's population density creates unique challenges, particularly concerning housing, traffic congestion, and air quality. The growth of Tehran also influences surrounding areas; for instance, the population of the provinces of Alborz and Tehran for 2006 and their average annual growth have been calculated based on data from 2006 and 2011, indicating a continuous expansion of the urban sprawl and its impact on neighboring administrative divisions. This intense concentration of people underscores the need for robust urban planning, sustainable development strategies, and efficient resource management to ensure the well-being of its vast population and to mitigate the environmental and social pressures that naturally arise from such high density.
Factors Influencing Iran's Population Dynamics
The trajectory of Iran's population density is shaped by a complex interplay of demographic factors, including birth rates, death rates, and migration patterns. These elements collectively determine the population growth rate, which indicates how fast a population is increasing or decreasing annually. While Iran has experienced significant growth in past decades, recent trends suggest a shift in these dynamics.
One notable demographic change is the increase in the average age of the population. In 1960, the average age was 23.9, which rose significantly to 34.2 by 2024. This aging trend implies a lower fertility rate, as a maturing population typically has fewer births relative to its total size. The concept of fertility rate, defined as the number of kids born per woman, is a critical component in understanding future population trends. While specific fertility rates are not provided in the data, the increasing average age strongly suggests a decline in the birth rate, which will inevitably impact future population growth and, consequently, population density.
Furthermore, socio-political events have also played a role in Iran's population dynamics, particularly concerning migration. Following the 1979 Iranian Revolution, over 5 million Iranians emigrated to other countries, forming a sizeable diaspora. While this outward migration might have temporarily alleviated some internal population pressures, its long-term impact on the country's demographic structure and the skills available within Iran is undeniable. These factors, combined with internal movements and government policies related to housing and development, continuously mold the country's population landscape.
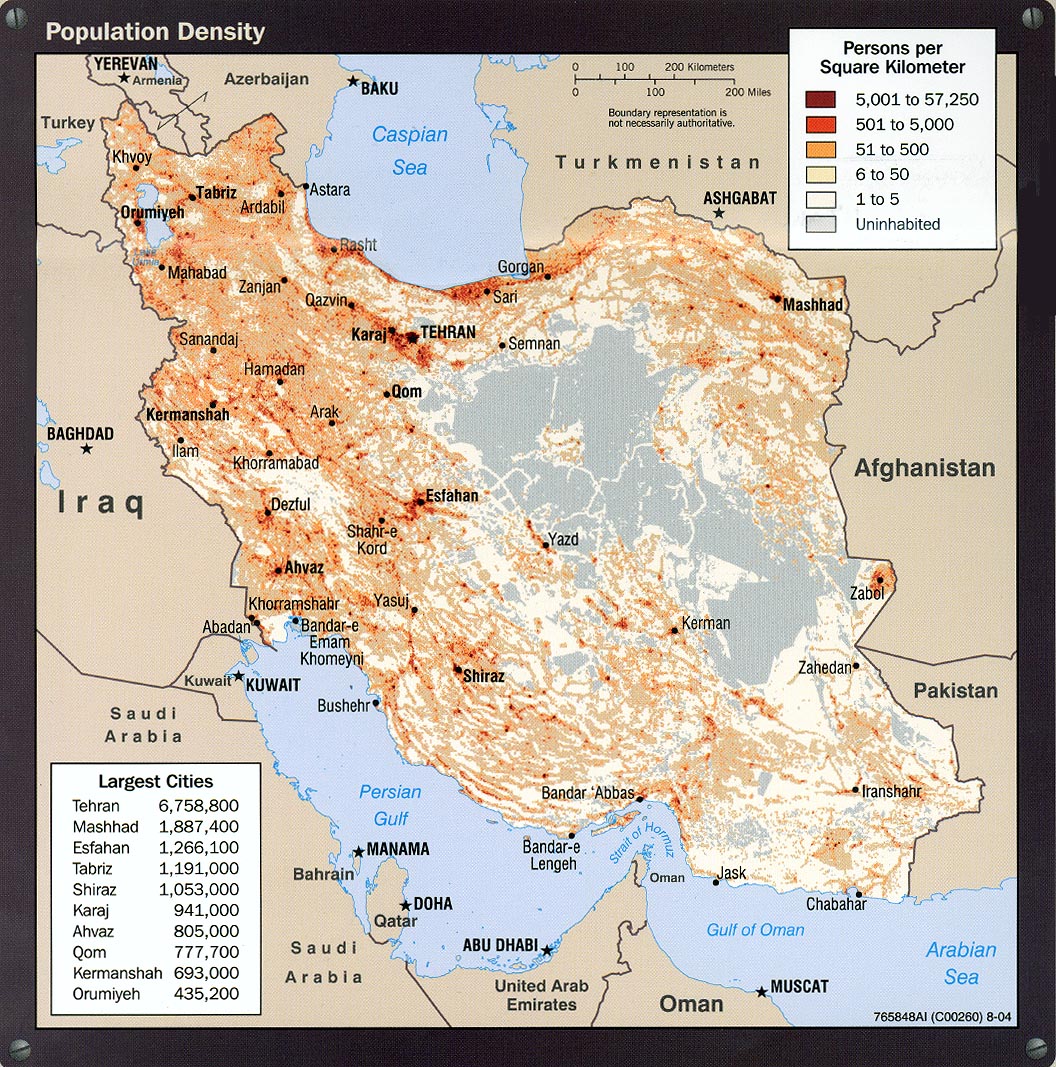
Regional Disparities in Population Density Across Iran
While national averages provide a broad understanding of population density in Iran, it is crucial to acknowledge the significant regional disparities that exist across its diverse provinces. Iran is a vast country with varied geographical features, including extensive deserts, rugged mountains, and fertile plains, which naturally influence where people choose to settle. This leads to vastly different population densities from one province to another, creating a mosaic of demographic distribution rather than a uniform spread.
Data from 2013 on the provinces of Iran by population density highlights these differences, although specific provincial figures are not detailed in the provided text. However, the mention of the ability to "Click on the column header brings the table in order of the column header" with "The default order is the province name" implies that detailed provincial data exists and would show a wide range. For instance, provinces with major urban centers like Tehran and Alborz (whose growth calculations for 2006 and 2011 were based on census data) would exhibit much higher densities compared to provinces dominated by arid landscapes or less developed rural areas. Understanding these regional variations is vital for targeted policy-making, ensuring that resource allocation, infrastructure development, and social services are tailored to the specific needs and demographic realities of each area, rather than a one-size-fits-all approach based solely on national averages.
Future Projections and What They Mean for Iran's Population Density
Looking ahead, the future trajectory of Iran's population density presents a fascinating and somewhat counter-intuitive picture compared to many developing nations. While the country has experienced consistent growth in density over the past decades, projections indicate a potential shift towards a decrease in the long term. Specifically, Iran (Islamic Republic of) is projected to reach a population density of 49.1452 people per square kilometer by the year 2100. This is a notable decline from the current figures, which hover around 56-57 people per km².
This projected reduction in population density is supported by the expectation that "Every year Iran population is expected to reduce by 23391 people." Such a trend would be influenced by a combination of factors, including continued declines in fertility rates, an aging population, and potentially ongoing emigration. The population growth rate, which considers birth rates, death rates, and migration, will be the ultimate determinant of this future density. A sustained low birth rate, combined with a stable or slightly increasing death rate due to an aging demographic, could lead to a natural population decline. These projections carry significant implications for long-term planning, including economic development, social welfare systems, and infrastructure investment, as a declining and aging population presents a different set of challenges and opportunities compared to one that is rapidly expanding.
Navigating the Challenges and Opportunities of Density
The evolving landscape of population density in Iran presents a multifaceted set of challenges and opportunities that demand strategic foresight and adaptive governance. On one hand, the concentration of populations in urban centers, as exemplified by Tehran, creates immense pressure on existing infrastructure, including transportation, housing, and utilities. High density can exacerbate environmental issues such as air pollution and water scarcity, especially in an arid country like Iran. It also places a significant burden on social services like healthcare and education, requiring substantial investment and efficient delivery mechanisms. The need for sustainable housing construction and urban planning becomes paramount to prevent overcrowding and maintain a reasonable quality of life.
On the other hand, population density, particularly in urban hubs, can foster economic dynamism and innovation. Densely populated areas facilitate the exchange of ideas, support diverse labor markets, and can lead to more efficient service delivery due to economies of scale. They become magnets for talent and investment, driving national economic growth. The projected future decrease in overall population density, while potentially easing some environmental pressures, also presents challenges related to an aging workforce and maintaining economic productivity. Therefore, Iran's approach to its population density must be balanced, focusing on smart urban growth, investing in rural development to mitigate excessive urbanization, and developing policies that support a healthy demographic structure for sustained national prosperity.
Conclusion
The journey through Iran's population density reveals a complex and dynamic demographic narrative. From its historical low points in the early 20th century to the significant growth and rapid urbanization witnessed in recent decades, Iran's population distribution has undergone profound transformations. We've seen how the current population density of around 56-57 people per square kilometer places Iran uniquely in the global context, balancing a large population with a vast landmass.
The remarkable rise of urban centers like Tehran, where one in ten Iranians reside, underscores the challenges and opportunities of concentrated populations. Looking ahead, the projected decrease in overall population density by 2100 suggests a future shaped by changing fertility rates and an aging population, necessitating proactive planning for housing, infrastructure, and social services. Understanding these intricate patterns of population density in Iran is not merely an academic exercise; it is fundamental to crafting effective policies that ensure sustainable development, equitable resource distribution, and an improved quality of life for all its citizens.
What are your thoughts on Iran's demographic shifts? Share your insights in the comments below, or explore other articles on our site to delve deeper into global demographic trends.
Iran Population Density Map - Iran • mappery

Iran Population Density (1970)

A population density over shaded relief map of Iran.by… – VisionViral.com