Unveiling Iran's Location: A Deep Dive Into Its Geographical Heart
Have you ever found yourself wondering, "Where is Iran on the map?" This question, seemingly simple, unlocks a fascinating journey into the heart of Western Asia, revealing a nation rich in history, diverse in geography, and strategically positioned at the crossroads of continents. Iran, a country often in the headlines, holds a pivotal place on the global stage, not just for its geopolitical significance but also for its profound cultural heritage and stunning natural landscapes. Understanding its precise location is the first step to appreciating its complexity and importance.
From its rugged mountain ranges to its expansive deserts and coastal plains, Iran's geography tells a story of ancient empires, trade routes, and enduring civilizations. This comprehensive guide will take you on an exploratory tour, pinpointing Iran's exact position on the world map, detailing its borders, exploring its diverse provinces, and highlighting key geographical and cultural features that make it truly unique. Prepare to discover the intricate layers that define this captivating nation, far beyond the headlines.
Table of Contents
- Iran's Strategic Crossroads: Where is Iran on the Map?
- The Geographical Tapestry of Iran
- Iran's Political and Administrative Landscape
- Unraveling Iran's Historical and Cultural Identity
- Iran on the World Map: Visualized
- Demographics, Economy, and Modern Iran
- Exploring Iran: Travel and Attractions
- Frequently Asked Questions About Iran
Iran's Strategic Crossroads: Where is Iran on the Map?
To truly grasp where Iran is on the map, we must first understand its classification within global geography. Iran is unequivocally located in Western Asia, often considered part of the Middle East, though historically and culturally, it also shares strong ties with Central Asia. This dual identity stems from its past as Persia, which for centuries was the dominant Central Asian power. Its strategic position is undeniable, serving as an important geographic bridge connecting Asia, Europe, and Africa.
When you look at a political map of Asia, Iran immediately stands out due to its significant landmass. It is a large country, bordered by a multitude of nations and two crucial bodies of water. To its north, it meets the shores of the Caspian Sea, the world's largest inland body of water. To its south, it extends along the Persian Gulf and the Gulf of Oman, vital waterways for global trade and energy. These maritime borders are as significant as its land borders, defining its access and influence.
Its land neighbors include Iraq and Turkey to the west, Armenia and Azerbaijan to the northwest, Turkmenistan to the northeast, and Afghanistan and Pakistan to the east. This extensive network of borders underscores Iran's role as a regional nexus, influencing and being influenced by a diverse array of cultures, economies, and political landscapes. This intricate web of connections is fundamental to understanding where Iran is on the map, not just geographically but geopolitically as well.
The Geographical Tapestry of Iran
Iran's geography is remarkably diverse, a blend of rugged mountains, vast deserts, and fertile plains, all contributing to its unique character. This varied terrain is a direct result of its location on major tectonic plates, leading to a landscape characterized by dramatic elevation changes and distinct climatic zones. Understanding this physical geography is key to comprehending the distribution of its population, its historical development, and its economic activities. It's a country that truly embodies geographical contrasts.
Rugged Mountainous Terrain
A defining feature of Iran's physical map is its extensive mountain ranges. The country is characterized as having rugged terrain along its rim, forming natural barriers and creating distinct regions. Three major mountain chains dominate the landscape:
- The Elburz Mountains: These majestic mountains lie in the north, running parallel to the Caspian Sea. They form a formidable barrier between the sea and the Iranian plateau, influencing rainfall patterns and creating a lush, humid climate along the Caspian coast, a stark contrast to the arid interior. Mount Damavand, the highest peak in Iran and the Middle East, is part of this range, an iconic symbol of the nation.
- The Zagros Mountains: Stretching from the northwest to the southeast, the Zagros range forms Iran's longest mountain chain. These mountains are known for their deep valleys, rich biodiversity, and historical significance, having served as a cradle for early civilizations.
- The Kuh Rud Mountains: Spanning the interior of Iran, these mountains are part of the central Iranian plateau, contributing to the country's diverse topography. They separate the central deserts and influence the climate of the surrounding areas.
These mountain ranges have historically provided natural defenses, shaped regional cultures, and continue to be vital for water resources, supporting agriculture and human settlements in their valleys and foothills. They are an integral part of understanding where Iran is on the map, not just as a political entity but as a physical landmass.
Coastal and Desert Plains
Beyond the towering peaks, Iran's geography also encompasses vast plains and arid deserts. It’s a mix of deserts and plains along the coastal areas, particularly along the Persian Gulf and the Caspian Sea. The Caspian Sea coast, in particular, is characterized by its narrow plains, which are among the most fertile and densely populated regions due to abundant rainfall and moderate temperatures.
In contrast, the interior of the Iranian plateau is dominated by two major desert basins: the Dasht-e Kavir (Great Salt Desert) and the Dasht-e Lut (Empty Desert). These vast, inhospitable areas are among the hottest and driest places on Earth, characterized by salt flats, sand dunes, and extreme temperatures. Despite their harsh conditions, these deserts have played a role in Iran's history, acting as natural barriers and influencing trade routes and settlement patterns. The presence of such contrasting geographical features within one nation truly highlights the incredible diversity of Iran's landscape.
Iran's Political and Administrative Landscape
Beyond its physical features, understanding where Iran is on the map also involves delving into its political and administrative divisions. Iran is divided into 31 provinces, each with its own capital city, contributing to the nation's rich tapestry of local cultures, economies, and traditions. These administrative divisions are crucial for governance, resource management, and understanding the distribution of its large population.
Tehran: The Beating Heart and Capital
At the heart of Iran's political and economic life lies Tehran, its bustling capital city. Located in the northern part of the country, at the foot of the Alborz Mountains, Tehran is a sprawling metropolis and one of the largest cities in Western Asia. It serves as the political, cultural, economic, and industrial center of Iran, a vibrant hub where modernity intertwines with ancient traditions.
Tehran's strategic location, its vast population, and its role as the seat of government make it a focal point for understanding the nation. It's where national policies are formulated, major industries operate, and a significant portion of Iran's diverse population resides. The city's growth reflects Iran's demographic shifts and its ongoing development, making it an essential landmark when considering where Iran is on the map of global urban centers.
Provinces and Major Cities
Iran's provinces, such as Fars, Isfahan, Khorasan Razavi, and Gilan, each boast unique characteristics and contribute to the country's rich diversity. Major cities like Mashhad, Isfahan, Shiraz, Tabriz, and Qom are not just administrative centers but also historical and cultural powerhouses, each with its own distinct identity and attractions.
- Mashhad: Located in the northeast, it is Iran's second-largest city and a major pilgrimage site for Shia Muslims.
- Isfahan: Situated in central Iran, it is renowned for its stunning Islamic architecture, beautiful bridges, and vibrant bazaars, often considered a jewel of Persian culture.
- Shiraz: In the southwest, it is celebrated for its gardens, poetry, and historical sites, including the nearby Persepolis.
- Tabriz: In the northwest, it is a historic city known for its grand bazaar, a UNESCO World Heritage site, and its rich Azerbaijani culture.
These cities, along with their respective provinces, showcase the vast cultural and geographical variations across Iran. From the Caspian Sea's lush greenery to the ancient ruins of Fars province, each region offers a unique glimpse into the country's multifaceted identity. Exploring these significant states, provinces/districts, and cities provides a deeper understanding of the nation's internal structure and cultural richness.
Unraveling Iran's Historical and Cultural Identity
Iran's location on the map is inextricably linked to its profound history and vibrant culture. Formerly known as Persia, this ancient land has been a cradle of civilization for millennia, giving rise to powerful empires that shaped much of the ancient world. The Persian Empire, in particular, was the dominant Central Asian power for many centuries, leaving an indelible mark on art, architecture, philosophy, and governance.
The country's rich history is reflected in its numerous UNESCO World Heritage sites, ancient ruins, and historical landmarks that dot the landscape. From the majestic ruins of Persepolis, the ceremonial capital of the Achaemenid Empire, to the intricate mosques and palaces of Isfahan, Iran offers a journey through time. Its culture is a vibrant tapestry woven from Persian, Islamic, and regional influences, expressed through its exquisite poetry, intricate carpets, traditional music, and diverse culinary traditions.
Religion, primarily Shia Islam, plays a central role in Iranian society and culture, influencing daily life, traditions, and national identity. However, Iran also has a history of religious diversity, with minority communities coexisting for centuries. Understanding this deep historical and cultural context is vital when trying to comprehend where Iran is on the map, not just geographically but in the broader human narrative.
Iran on the World Map: Visualized
Seeing where Iran is on the world map provides the clearest understanding of its global position. Illustrated on a blue ocean laminated map of the world, Iran typically appears prominently in red, highlighting its strategic position in the Middle East. This type of map often shows a combination of political and physical features, including country boundaries, major cities, major mountains in shaded relief, and ocean depth in blue color gradient, along with many other features.
Interactive maps, such as Open Street Map or Google Maps, offer an even more dynamic way to explore Iran's exact location. You can zoom in or out to see the surrounding area, drag the map with your mouse or finger to see surrounding objects, and even check out Iran on a satellite map for a real-world perspective. These tools allow for an in-depth exploration of its topography, urban centers, and natural features, making the concept of "where is Iran on the map" tangible and immediate.
Various specialized maps further enhance our understanding: political maps delineate its provinces and cities, administrative maps detail its internal governance, physical maps highlight its mountains and deserts, tourist maps showcase its attractions, and road maps guide navigation. This comprehensive map atlas allows one to learn about Iran's location, history, culture, and attractions from multiple perspectives.
The comparison with other countries, like Israel, also puts Iran's scale into perspective. The first thing to note is that Iran is much, much bigger than Israel (around 75x bigger). It also has lots more people. This vastness contributes to its diverse climates, landscapes, and regional variations, making it a country of immense internal contrasts.
Additionally, some maps focus on specific aspects, such as the location of nuclear mining and fuel processing facilities, power reactors, nuclear research and development, and suspected weaponization research facilities. While these maps are highly specialized, they underscore the strategic importance of certain geographical points within Iran and how its location plays a role in international affairs.
Demographics, Economy, and Modern Iran
Understanding where Iran is on the map also requires an appreciation of its human geography – its population and economy. With a population exceeding 80 million people, Iran is one of the most populous countries in the Middle East. This large and diverse population contributes to its dynamic society, rich cultural expressions, and significant workforce. The demographics are influenced by various factors, including its varied climate zones and the distribution of natural resources.
Iran's economy is largely driven by its vast oil and natural gas reserves, making it a major player in the global energy market. However, the country also has a diversified economy that includes agriculture, manufacturing, and services. Its strategic location facilitates trade routes, connecting it to markets in Asia, Europe, and Africa. Despite challenges, Iran continues to develop its infrastructure, industries, and technological capabilities, aiming for greater economic self-sufficiency and regional integration.
The country's official symbol, seal, and flag are important national identifiers, reflecting its history, culture, and political system. Furthermore, understanding practical details like postal/area/zip codes and time zones (Iran Standard Time, UTC+3:30) is essential for anyone dealing with the country, whether for business, travel, or personal connections. These elements, though seemingly minor, are crucial components of Iran's identity on the global stage.
Exploring Iran: Travel and Attractions
For those intrigued by where Iran is on the map and eager to explore its wonders, the country offers an incredible array of travel destinations and attractions. Its diverse geography translates into a variety of landscapes, from ski resorts in the Alborz Mountains to ancient desert cities and pristine Persian Gulf islands.
Some of Iran's most famous travel destinations and attractions include:
- Persepolis: The ancient capital of the Achaemenid Empire, a UNESCO World Heritage site, offering breathtaking ruins and a glimpse into Persia's glorious past.
- Naqsh-e Jahan Square (Isfahan): Another UNESCO site, one of the largest city squares in the world, surrounded by stunning Safavid-era architecture, including the Imam Mosque and Ali Qapu Palace.
- Shiraz: Known as the city of poets, gardens, and nightingales, home to the tombs of Hafez and Saadi, and the beautiful Eram Garden.
- Yazd: A unique desert city with traditional Persian architecture, ancient windcatchers, and Zoroastrian fire temples, a UNESCO World Heritage city.
- Kish Island: A free trade zone in the Persian Gulf, offering modern resorts, shopping, and water sports, a popular destination for domestic tourism.
- Tabriz Historic Bazaar Complex: One of the oldest bazaars in the Middle East and a UNESCO World Heritage site, a vibrant center of trade and culture.
These attractions, coupled with Iran's rich cultural heritage, warm hospitality, and delicious cuisine, make it a compelling destination for adventurous travelers. Discovering these places on a tourist map of Iran truly brings its geographical and cultural richness to life.
Frequently Asked Questions About Iran
To further clarify common misconceptions and provide a holistic view of where Iran is on the map, here are answers to some frequently asked questions:
- Why is Iran not in Africa? Iran is definitively located in Western Asia, bordering the Middle East. Its geographical coordinates place it firmly on the Asian continent, separated from Africa by the Arabian Peninsula and the Red Sea. There is no geographical basis for it to be considered part of Africa.
- What is Farsi? Farsi is the official language of Iran. It is also known as Persian and is an Indo-Iranian language, a branch of the Indo-European language family. It has a rich literary tradition, with famous poets like Rumi, Hafez, and Saadi.
- What is Iran's official name? The official name is the Islamic Republic of Iran. Prior to 1935, it was widely known as Persia in the Western world.
- Does Iran have nuclear facilities? Yes, Iran has nuclear facilities, including mining, fuel processing, power reactors, and research and development sites. The locations of these facilities are often depicted on specialized maps due to their international significance.
Conclusion
Understanding where Iran is on the map is far more than simply pointing to a spot on a globe. It's an exploration into a country of immense geographical diversity, profound historical depth, and vibrant cultural richness. From its strategic position bridging Asia, Europe, and Africa, bordered by the Caspian Sea and the Persian Gulf, to

Israel Vs Iran - Brilliant Maps
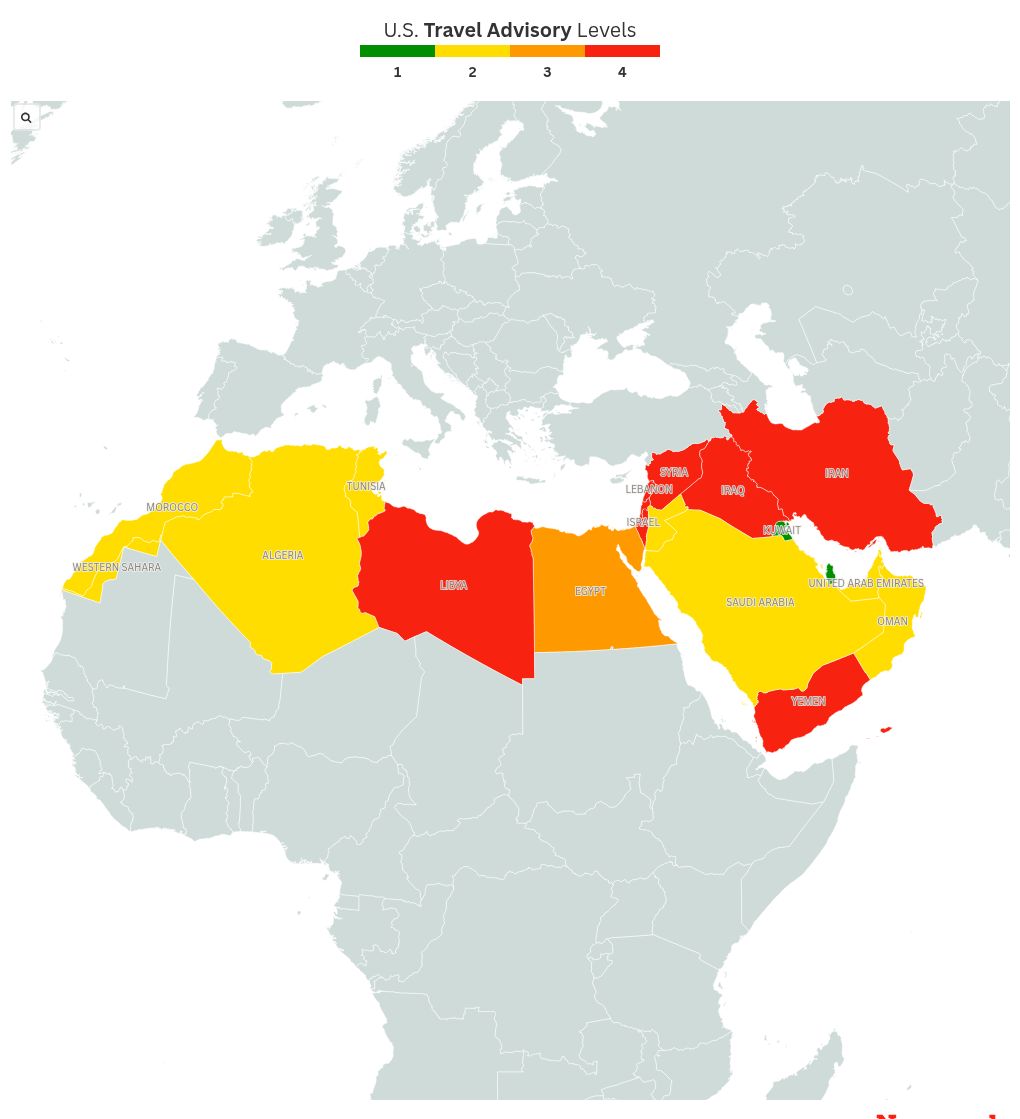
Map Shows U.S. Middle East Travel Warnings as Possible Iran War Looms
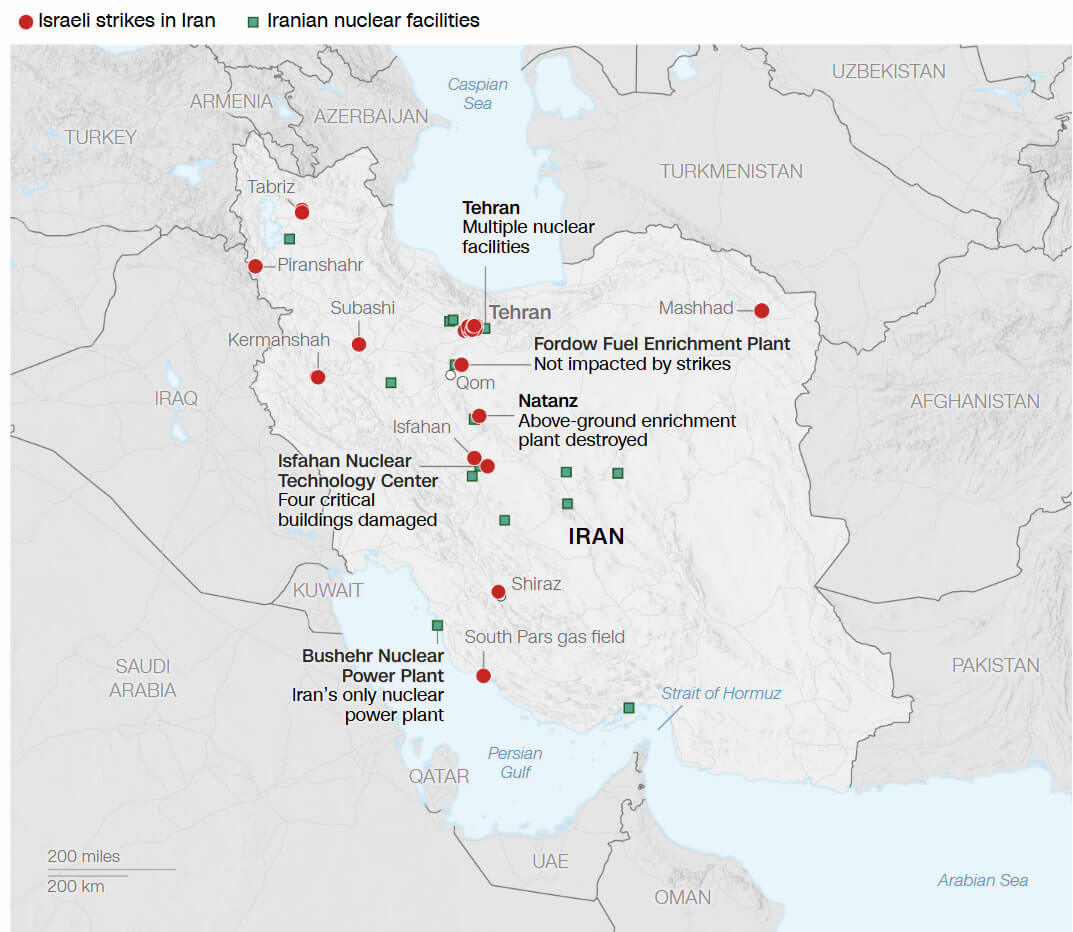
Iran Israel War Map - Location Strikes Map in Iran and Israel - Guide