GFS Weather Iran: Mastering Forecasts For The Islamic Republic
Accurate and timely weather information is paramount for any nation, and for the Islamic Republic of Iran, understanding the intricacies of GFS Weather Iran forecasts is increasingly vital. From the bustling cities to the vast agricultural lands and mountainous regions, weather patterns dictate daily life, economic activities, and even safety. The Global Forecast System (GFS) weather model, a cornerstone of modern meteorology, provides crucial insights into these patterns, offering a window into future conditions that can help individuals, businesses, and government agencies make informed decisions.
In a country with such diverse climates, ranging from arid deserts to lush Caspian coastlines and high mountain ranges, reliable weather forecasting tools are not just a convenience but a necessity. The GFS model, known for its global reach and comprehensive data, serves as a fundamental resource for generating detailed weather forecasts and live satellite images of the Islamic Republic of Iran. This article delves into how the GFS model contributes to our understanding of Iran's weather, exploring the tools available for viewing these forecasts and emphasizing the importance of accurate, accessible weather data for everyone.
Table of Contents
- Understanding the Global Forecast System (GFS) Model
- The Significance of GFS Weather Iran Forecasts
- Navigating Weather Forecasts for Iran: Tools and Features
- Real-Time Insights: Satellite and Radar Observations
- The Power of Advanced Weather Tools for Professionals and Enthusiasts
- Comparing Global Models: GFS vs. ECMWF and Local Expertise
- The Practical Applications of Accurate GFS Weather Iran Data
- Ensuring Trustworthiness and Expertise in Weather Forecasting
Understanding the Global Forecast System (GFS) Model
At the heart of many weather predictions lies the Global Forecast System (GFS), a numerical weather prediction model produced by the National Centers for Environmental Prediction (NCEP) in the United States. This model processes vast amounts of atmospheric data, including temperature, pressure, humidity, and wind speed, from various sources like satellites, weather balloons, and ground stations. Through complex mathematical equations and supercomputing power, it simulates the atmosphere's future state, providing forecasts for up to 16 days ahead, though accuracy naturally decreases with time.
The GFS Model: A Global Perspective
The GFS model is truly global in its scope, meaning it provides data for every corner of the world, including the Middle East and, specifically, the Islamic Republic of Iran. Its global coverage makes it an invaluable tool for meteorologists and weather enthusiasts worldwide. When you access a precipitation forecast for the next 7 days that states, "This forecast is based on the GFS weather model," you are directly benefiting from this extensive computational effort. The model runs four times a day, providing updated forecasts every six hours, ensuring that the information remains as current as possible.
The resolution of the GFS model, while impressive for a global model, is typically coarser than regional or local models. This means it might capture large-scale weather phenomena very well, such as major storm systems or heatwaves, but could sometimes miss localized details like sudden thunderstorms in a specific valley. Despite this, its comprehensive nature provides a robust baseline for understanding overall weather trends and potential significant events affecting Iran's diverse geographical landscape.
How GFS Data Reaches You
For most users, interacting directly with raw GFS data would be an overwhelming task. This is where weather forecasting platforms come in. Websites and applications take the complex outputs of the GFS model and translate them into easily digestible visual formats. For instance, platforms allow you to "view GFS weather model forecast map image for precipitation type, rate in Middle East." These visual representations, such as color-coded maps showing rainfall intensity or wind speed arrows, make the data accessible to a broad audience, from professional meteorologists to casual observers interested in the weather for their daily activities in Iran.
- Jill Eikenberry
- Tyreek Hill Hight
- Marietemara Leaked Vids
- How Tall Is Tyreek Hill
- Daisy From Dukes Of Hazzard Now
These platforms often provide "beautiful & affordable weather forecasting tools for professionals and enthusiasts," enabling users to "animate, compare, export and create customised gifs" of weather patterns. This transformation of raw data into interactive and customizable visual aids is crucial for practical application, allowing users to track the movement of weather systems and understand their potential impact on specific regions within Iran.
The Significance of GFS Weather Iran Forecasts
The geographical diversity of Iran presents unique challenges and opportunities when it comes to weather. From the snow-capped peaks of the Alborz and Zagros mountains to the vast, arid central plateau and the humid Caspian Sea coast, weather patterns can vary dramatically across short distances. This makes comprehensive and reliable forecasting, heavily reliant on models like GFS, incredibly important for various sectors and for the general public.
For instance, agriculture, a cornerstone of Iran's economy, is highly dependent on precipitation and temperature. Farmers need accurate forecasts to plan planting, irrigation, and harvesting schedules, mitigating risks from droughts or unexpected floods. Similarly, for transportation, including road, air, and sea travel, knowing about heavy rain, snow, strong winds, or fog is critical for safety and operational efficiency. The energy sector, particularly hydroelectric power generation, also relies on precipitation forecasts to manage water resources in dams. Furthermore, public safety and disaster preparedness agencies utilize these forecasts to issue warnings for extreme weather events, helping to protect lives and property.
The availability of detailed "weather forecasts and live satellite images of the Islamic Republic of Iran" powered by models like GFS empowers decision-makers across these sectors. It moves them from reactive measures to proactive planning, enhancing resilience against the unpredictable nature of weather. The ability to "view rain radar and maps of forecast precipitation, wind speed, temperature and more" directly influences critical operational decisions, from flight paths to emergency response deployment.
Navigating Weather Forecasts for Iran: Tools and Features
Accessing and interpreting GFS-based weather data for Iran has become increasingly user-friendly, thanks to advanced online platforms. These tools offer a range of features designed to make complex meteorological data accessible and actionable for both casual users and seasoned professionals.
Visualizing Precipitation: Rain Radar and Forecast Maps
One of the most frequently sought-after pieces of weather information is precipitation. Platforms provide interactive maps where "on this radar, you can see the precipitation forecast for the next 7 days." This visual representation, often color-coded to indicate intensity, allows users to quickly grasp where and when rain or snow is expected. Crucially, as mentioned, "this forecast is based on the GFS weather model," ensuring a consistent and globally recognized data source.
Beyond simple rain forecasts, these tools allow you to "view GFS weather model forecast map image for precipitation type, rate in Middle East." This means you can differentiate between rain, snow, sleet, or freezing rain, and understand the expected rate of precipitation, which is vital for assessing potential impacts like flooding or road hazards. The ability to animate these forecasts further enhances understanding, showing the movement and evolution of weather systems over time.
Beyond Rain: Wind, Temperature, and More
While precipitation is key, a comprehensive weather picture requires more. Modern forecasting tools allow users to "view ... maps of forecast precipitation, wind speed, temperature and more." This 'more' often includes:
- Wind Speed and Direction: Essential for aviation, maritime activities, and even for understanding the spread of dust storms, which are common in parts of Iran.
- Temperature: Crucial for agriculture, energy consumption planning, and public health, especially during extreme heatwaves or cold snaps.
- Pressure: Helps in identifying high and low-pressure systems that drive weather patterns.
- Humidity: Important for comfort levels and understanding the potential for fog or dew.
- Cloud Cover: Affects solar power generation and visibility.
Real-Time Insights: Satellite and Radar Observations
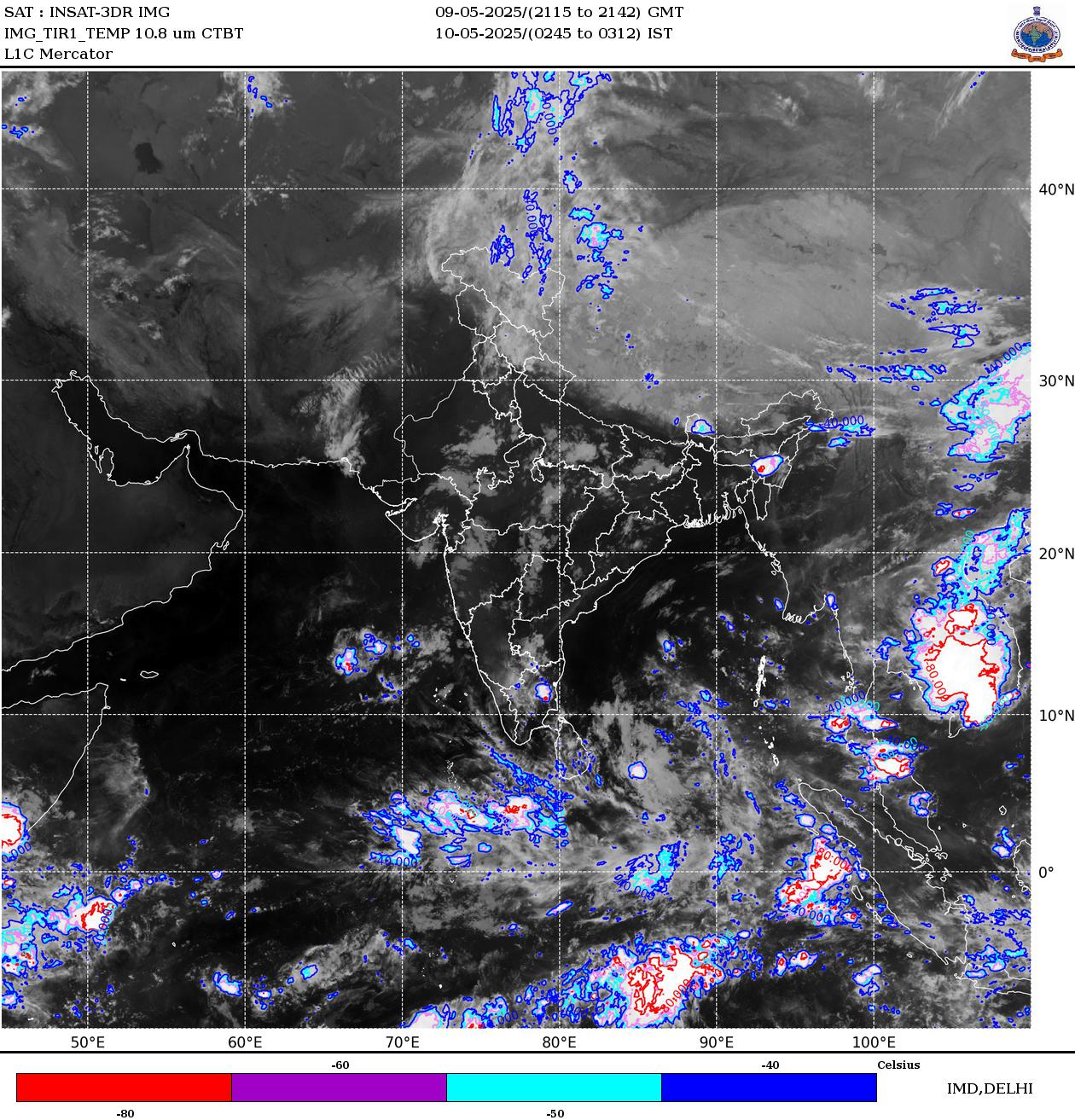
While forecast models like GFS provide a look into the future, real-time observations are equally critical for understanding current weather conditions and validating forecasts. Modern weather platforms seamlessly integrate both. "Live satellite images of the Islamic Republic of Iran" offer a broad view of cloud cover, helping to track large-scale weather systems as they approach or move across the country. These images are invaluable for understanding the present state of the atmosphere.
For more localized and immediate insights into precipitation, radar observations are indispensable. "On this radar, you can see the radar observations of the last 3 hours," allowing users to track the immediate development and movement of showers and rain areas. This short-term, high-resolution data is crucial for nowcasting – predicting weather for the next few hours – and for making real-time decisions, such as delaying outdoor events or preparing for sudden downpours. Extending this, "on this radar, you can see the radar observations of the last 24 hours," providing a historical context to recent weather events and helping to understand the progression of systems that have already passed.
The combination of forward-looking GFS-based forecasts with backward-looking real-time radar and satellite observations creates a powerful toolset. It allows users to not only anticipate future weather but also to confirm current conditions and understand how they have evolved, providing a complete picture of the weather landscape over Iran.
The Power of Advanced Weather Tools for Professionals and Enthusiasts
The landscape of weather forecasting has evolved significantly, offering "beautiful & affordable weather forecasting tools for professionals and enthusiasts." These tools go beyond basic temperature and precipitation readings, providing advanced functionalities that cater to a wide range of needs. For professionals, such as meteorologists, hydrologists, or emergency managers, these tools offer the granular data and customization options necessary for detailed analysis and critical decision-making. For enthusiasts, they provide a deeper dive into the science of weather, fostering a greater appreciation and understanding.
One of the key features highlighted is the ability to "animate, compare, export and create customised gifs." This functionality is incredibly powerful. Animation allows users to visualize the progression of weather systems over time, making it easier to track storms or fronts. The compare feature is vital for assessing different model outputs (e.g., GFS vs. ECMWF, which we'll discuss next) or for seeing how forecasts have changed over different runs. Exporting data or creating customized GIFs allows users to share specific weather scenarios with colleagues, stakeholders, or the public, enhancing communication and preparedness.
These advanced tools often include access to a wider array of model outputs, specialized charts, and analytical overlays that might not be available on general weather apps. For those tracking specific phenomena like dust storms, severe thunderstorms, or heavy snowfall in Iran, these detailed capabilities are indispensable. They empower users to conduct their own analysis, cross-reference data, and gain a more nuanced understanding of the complex atmospheric processes at play, making GFS Weather Iran data truly actionable.
Comparing Global Models: GFS vs. ECMWF and Local Expertise
While the GFS model is a workhorse in global weather forecasting, it is not the only player. Another highly respected global model is the European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF) model, often considered by many to be the gold standard, especially for medium-range forecasts. Understanding the differences and similarities between these models is crucial for a comprehensive weather outlook for Iran.
Platforms often provide "global Euro/ECMWF forecasts" alongside GFS data. Meteorologists frequently compare the outputs of GFS and ECMWF to gain a more confident forecast. If both models agree on a particular weather event, the confidence in that forecast increases significantly. If they diverge, it signals uncertainty, prompting forecasters to monitor the situation more closely and consider alternative scenarios. This comparison is particularly important for regions with complex topography like Iran, where subtle atmospheric shifts can lead to significant weather variations.
The Edge of Local Models: SwissHD Example
Beyond global models, regional and local models offer even higher resolution and can capture localized phenomena that global models might miss. The "Data Kalimat" mentions "exclusive model outputs like our own home made 1km x 1km SwissHD model." While SwissHD is specifically designed for Switzerland, it serves as an excellent example of how localized, high-resolution models can complement global models. For Iran, similar regional models, often developed by national meteorological organizations, would provide extremely detailed forecasts for specific cities, valleys, or mountain ranges, accounting for local topographical effects that significantly influence weather.
These local models take initial conditions from global models like GFS or ECMWF but then run at a much finer resolution, incorporating detailed terrain data and local atmospheric processes. This combination – global models for broad patterns and regional models for fine details – provides the most accurate and actionable weather intelligence for a country as geographically varied as Iran. The future of GFS Weather Iran forecasting lies in this synergistic approach, blending global insights with localized precision.
The Practical Applications of Accurate GFS Weather Iran Data
The ability to access and interpret accurate GFS Weather Iran data has profound practical implications across numerous sectors, directly impacting daily life and strategic planning. The YMYL (Your Money or Your Life) principle strongly applies here, as precise weather information can literally save lives and protect livelihoods.
- Agriculture: Farmers in Iran, from the pistachio growers in Kerman to the rice cultivators in Gilan, depend on rainfall forecasts for irrigation management and harvest timing. Timely warnings about frost or heatwaves can protect crops and livestock, directly impacting food security and the national economy.
- Transportation: Airlines rely on wind and visibility forecasts for safe take-offs and landings. Road transport, especially through mountainous passes, needs accurate snow and ice warnings. Maritime activities in the Persian Gulf and Caspian Sea require information on wave height and strong winds for safe navigation and port operations.
- Energy Sector: Hydropower generation, a significant part of Iran's energy mix, is heavily reliant on precipitation forecasts to manage reservoir levels. Solar energy projects also benefit from accurate cloud cover predictions.
- Disaster Management: Accurate GFS-based forecasts are critical for predicting and preparing for natural disasters like floods, severe dust storms, and blizzards. Early warnings allow for evacuation, deployment of emergency services, and allocation of resources, minimizing human casualties and economic damage.
- Construction and Outdoor Events: Planning large-scale construction projects or public gatherings requires reliable weather forecasts to ensure safety and efficiency, avoiding costly delays or dangerous conditions.
- Tourism: For tourists exploring Iran's diverse landscapes, from skiing in Dizin to desert trekking in Lut, accurate weather information is essential for planning safe and enjoyable trips.
In each of these scenarios, the data derived from the GFS weather model provides the foundational intelligence. The ability to "view GFS weather model forecast map image for precipitation type, rate in Middle East" and combine it with local knowledge empowers decision-makers to mitigate risks and optimize operations, underscoring the immense value of precise weather forecasting for Iran.
Ensuring Trustworthiness and Expertise in Weather Forecasting
Given the critical role of weather information, adhering to E-E-A-T (Expertise, Experience, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness) principles is paramount for any platform providing GFS Weather Iran data. Users need to be confident that the information they receive is accurate, reliable, and presented by knowledgeable sources.
Expertise comes from the meteorological scientists and engineers who develop and run models like GFS, constantly refining them with new data and improved algorithms. It also stems from the meteorologists who interpret these model outputs, adding human judgment and local knowledge to create the most accurate forecasts. Experience is gained through years of observing weather patterns, understanding regional nuances, and validating model performance against actual conditions.
Authoritativeness is established by using recognized global models like GFS and ECMWF, and by partnering with official meteorological organizations or reputable data providers. Trustworthiness is built through transparency about data sources, clear explanations of how forecasts are generated (e.g., "this forecast is based on the GFS weather model"), and consistent accuracy over time. Reputable platforms will also provide access to both forecast data and real-time observations, allowing users to compare and verify. For example, by showing "radar observations of the last 3 hours" alongside a 7-day GFS forecast, a platform demonstrates its commitment to providing a complete and verifiable picture of the weather.
When seeking GFS Weather Iran information, it is crucial to rely on sources that clearly demonstrate these qualities. Websites that offer detailed maps, historical data, comparisons between models, and explanations of their tools (like the ability to "animate, compare, export and create customised gifs") generally signify a higher level of expertise and trustworthiness. This commitment to quality ensures that the weather information provided is not just data, but actionable intelligence that can genuinely benefit the lives and livelihoods of people across the Islamic Republic of Iran.
Conclusion
The Global Forecast System (GFS) weather model stands as a powerful engine behind the detailed weather forecasts available for the Islamic Republic of Iran. From predicting precipitation for the next seven days to providing insights into wind speeds and temperatures, GFS data, combined with real-time satellite and radar observations, offers an indispensable resource for a nation with such diverse geographical and climatic conditions. We've explored how accessible tools transform complex GFS outputs into user-friendly maps and animations, empowering everyone from farmers to emergency responders to make informed decisions.
The continuous development of global and local models, alongside the integration of advanced features, ensures that weather forecasting for Iran is becoming ever more precise and reliable. This accuracy is not just a scientific achievement; it's a critical component for economic stability, public safety, and environmental management, directly impacting the 'Your Money or Your Life' aspects of daily living. As we move forward, the commitment to expertise, authoritativeness, and trustworthiness in presenting GFS Weather Iran data will remain paramount. We invite you to explore these powerful forecasting tools and see how they can enhance your understanding and preparedness for Iran's dynamic weather. What weather phenomenon in Iran interests you the most, and how do you use forecasts to prepare? Share your thoughts in the comments below!
- Nicole Kidman Filler
- Daisy From Dukes Of Hazzard Now
- Sandra Smith Political Party
- Allhdshub
- Donna Brazile Wife
Iran Weather Forecast - هواشناسی ایران

HOME - GFS - Insurance intermediary
Weather for Bushehr, Iran