Unpacking Iran's 2023 GDP: Growth, Resilience, And Economic Insights
Understanding a nation's economic health often begins with its Gross Domestic Product (GDP), a comprehensive measure of all goods and services produced within its borders. For Iran, a country frequently navigating complex geopolitical and economic currents, the Iran GDP for 2023 offers a crucial lens into its performance and resilience. This figure is not just a number; it reflects the collective output of its industries, the spending patterns of its people, and the strategic decisions of its government.
The economic narrative of Iran is one of remarkable adaptability. Despite facing significant external pressures and internal challenges, the country's economy continues to evolve, demonstrating periods of notable growth alongside its struggles. Delving into the 2023 GDP figures, along with historical data and future projections, provides invaluable insights for economists, policymakers, investors, and anyone interested in the dynamics of the Middle Eastern economy. This article aims to break down the key components of Iran's 2023 GDP, offering a clear, data-driven perspective on its economic standing.
Table of Contents
- Iran's Economic Landscape in 2023: An Overview
- Unpacking GDP Growth Rates: A Closer Look at 2023 and Beyond
- GDP Per Capita: What It Means for the Average Iranian
- Iran's Position in the Global Economy
- Deconstructing Iran's GDP by Expenditure
- National Defense Spending: A Significant Allocation
- Historical Context and Future Projections
- Conclusion: Navigating the Future of Iran's Economy
Iran's Economic Landscape in 2023: An Overview
The most striking figure concerning Iran's economic performance in 2023 is its Gross Domestic Product (GDP). According to official data from the World Bank, the **Iran GDP for 2023 was 404.63 billion US dollars**. This substantial figure represents a 2.6% increase from the previous year, signaling continued, albeit moderate, economic expansion. To put this into a global perspective, this GDP value accounts for approximately 0.38 percent of the entire world economy, underscoring Iran's significant, though not dominant, role on the global economic stage. Looking back, the Iranian economy has demonstrated a pattern of consistent growth in recent years. In 2022, Iran's GDP stood at 394.36 billion US dollars, marking a 2.85% increase from 2021. The year 2021 itself saw a GDP of 383.44 billion US dollars, which was a remarkable 46.25% increase from 2020. This significant jump in 2021 highlights a period of strong recovery or accelerated growth, potentially rebounding from earlier economic contractions. These figures, compiled from officially recognized sources like the World Bank's collection of development indicators, provide a robust foundation for analyzing Iran's economic trajectory. The consistent upward trend, even if varying in pace, suggests an underlying resilience within the Iranian economic framework.Unpacking GDP Growth Rates: A Closer Look at 2023 and Beyond
Beyond the nominal GDP figure, the growth rate offers deeper insights into the dynamism of an economy. For **Iran's GDP in 2023**, the growth rate was reported at 5.04%. This represents a notable acceleration compared to the 3.78% growth rate recorded in 2022. The 2023 growth translates to an impressive change of 24.662 billion US dollars over 2022, when the real GDP was 488.865 billion US dollars. This upward trend in growth rates is a positive indicator, suggesting increasing economic activity and potentially improved conditions for businesses and individuals. It's crucial to differentiate between nominal and real GDP. While the nominal GDP provides a current market value, real GDP adjusts for inflation, offering a clearer picture of actual economic output. The real GDP (constant, inflation-adjusted) of the Islamic Republic of Iran reached a substantial $513.527 billion in 2023. This figure, higher than the nominal GDP, indicates that the economy's expansion is not solely due to price increases but reflects genuine growth in goods and services produced. The consistent growth, even if fluctuating, underscores the ongoing efforts within Iran to bolster its domestic economy and navigate global economic headwinds.Historical Growth Trajectories and Revisions
Examining the historical context of Iran's GDP growth rates reveals a dynamic pattern. The 2022 growth rate of 3.78% was actually a slight decline from the 4.72% observed in 2021. However, 2021's growth itself was a significant 1.39% increase from the 3.33% recorded in 2020, which had seen a robust 6.4% increase from 2019. This ebb and flow highlight the various internal and external factors influencing Iran's economic performance over time. Interestingly, there have been revisions to past growth estimations. The entity responsible for these statistics revised its estimation for Iran’s economic growth in 2022, putting the country’s GDP growth for that year at 3.5 percent. This was an upward revision from an earlier calculation in an April report, which had put 2022's economic growth at 2.5 percent. The revised 3.5 percent growth of Iran’s economy in 2022 is particularly noteworthy as it is equal to the average growth of the world economy for that year, suggesting that Iran was growing in line with global trends despite its unique challenges. Over the broader decade leading up to 2023, the Iranian economy recorded an average annual growth of 2.3%, indicating a sustained, albeit moderate, expansion over the long term. This consistent growth, as highlighted in the Iran Economic Monitor, spring/summer 2023 report, shows that Iran’s economy continued to grow moderately for the third consecutive year in 2022/23, driven primarily by expansions in services and other key sectors.GDP Per Capita: What It Means for the Average Iranian
While overall GDP provides a picture of a nation's total economic output, GDP per capita offers a more granular view, indicating the average economic output per person. This metric is crucial for understanding the living standards and economic well-being of a country's population. For **Iran's GDP in 2023**, the per capita figure was reported at $4,466, according to the World Bank. This represents a 1.37% increase from 2022. Another source indicates Iran's GDP per capita in 2023 was approximately $5.67 thousand USD, up from $5.46 thousand USD in 2022. While there's a slight variation in these reported figures, both indicate an upward trend. Looking at the trend, Iran's GDP per capita for 2022 was $4,405, a 1.62% increase from 2021. The year 2021 saw a per capita GDP of $4,335, which was a significant 45.04% increase from 2020. This substantial jump in 2021 highlights a period of significant improvement in average economic output per person. Conversely, 2020 saw a per capita GDP of $2,989, which was a 21.99% decline from 2019, reflecting the economic challenges faced during that period, likely exacerbated by global events and sanctions. GDP per capita, calculated by dividing the gross domestic product by the mid-year population, provides a vital indicator of how economic growth translates into individual prosperity, or conversely, how economic downturns impact the average citizen. The recent increases suggest a gradual improvement in the economic opportunities and living conditions for the Iranian populace.Iran's Position in the Global Economy
Iran's economic size places it among the significant players on the world stage. In terms of nominal GDP, Iran is ranked number 41 among the 196 countries for which data is published. This ranking, based on a 2024 GDP figure of $401.357 billion, underscores its position as a medium-sized economy globally. However, when considering the purchasing power index (PPP), Iran's economic standing appears even more robust. According to the International Monetary Fund (IMF), Iran's GDP, based on the purchasing power index in 2023, reached an impressive $1.616 trillion. This figure represents a considerable $161 billion hike compared to the same period a year earlier. The IMF further positioned Iran at the 21st rank among the largest economies in the world in 2023, based on this PPP metric. This distinction is crucial because GDP at purchasing power parity adjusts for differences in the cost of living and inflation rates between countries, providing a more accurate comparison of real economic output and living standards. The higher ranking by PPP suggests that the actual purchasing power within Iran is significantly greater than what its nominal GDP might suggest, reflecting a stronger domestic economy capable of providing for its population. The IMF's comprehensive report, which includes the latest GDP figures for 194 countries, further solidifies Iran's substantial presence in the global economic landscape.Deconstructing Iran's GDP by Expenditure
Understanding how a nation's GDP is composed by expenditure provides critical insights into the structure of its economy and the primary drivers of its growth. For **Iran's GDP in 2023**, the breakdown by expenditure offers a clear picture of where economic activity is concentrated: * **Private Consumption:** This accounted for a substantial 47.2% of the GDP. This high percentage indicates that household spending on goods and services is the largest component of Iran's economy, signifying the importance of consumer demand in driving growth. * **Government Consumption:** Representing 13.2% of GDP, government spending on public services, administration, and other operational costs plays a significant, though smaller, role compared to private consumption. * **Fixed Investment:** This category, which includes spending on capital goods like machinery, buildings, and infrastructure, made up 36.4% of GDP. A high percentage in fixed investment is often a positive sign for future economic growth, as it indicates expansion of productive capacity. * **Net Exports:** This component, which is the value of exports minus imports, accounted for 3.2% of GDP. A positive net export figure means that Iran is exporting more goods and services than it is importing, contributing positively to its overall economic output. These figures highlight a consumer-driven economy with a strong emphasis on investment, suggesting a focus on both immediate demand and long-term productive capacity.The Role of Key Economic Sectors
While the expenditure breakdown offers a demand-side view, understanding the supply-side contribution of various economic sectors is equally important. Traditionally, Iran's economy has been heavily reliant on its vast oil and gas reserves. In 2023, the oil sector accounted for 8.6 percent of the GDP. While still a significant contributor, this percentage indicates a degree of diversification compared to historical periods where oil's share was much higher. This suggests ongoing efforts to develop non-oil sectors to reduce economic vulnerability to oil price fluctuations and international sanctions. Furthermore, the real GDP growth in 2022/23 was driven by expansions in services and other sectors. This points to a broadening of Iran's economic base, with the service industry playing an increasingly vital role in generating economic activity and employment. The growth in services, alongside other non-oil sectors, is a crucial element in building a more resilient and diversified economy, less susceptible to external shocks affecting the energy market.National Defense Spending: A Significant Allocation
National defense spending is an important component of government expenditure and can have a considerable impact on a nation's budget and economic priorities. According to official data, as of 2023, Iran allocated 10.3 billion USD to its national defense, which represents 2.1% of its GDP. This figure highlights the country's commitment to its security apparatus, a common feature in many nations with significant geopolitical roles. To provide context, this percentage is similar to that observed in other countries with well-established defense capabilities, such as the UK, France, and Finland. While the absolute amount may differ, the proportion of GDP dedicated to defense indicates a strategic allocation of resources. This spending can have ripple effects throughout the economy, supporting defense industries, creating employment, and driving technological advancements, even as it represents a significant portion of the national budget that could otherwise be allocated to other sectors like infrastructure, education, or healthcare. The decision to maintain a robust defense budget reflects the prevailing security concerns and strategic imperatives facing the nation.Historical Context and Future Projections
Understanding the current state of **Iran's GDP in 2023** is greatly enhanced by examining its historical trajectory and looking ahead at future projections. The economic journey of Iran has been marked by significant shifts over the decades. From 1980 to 2024, the country's GDP has risen by approximately 305.51 billion US dollars, illustrating substantial long-term growth despite periods of volatility and external pressures. This long-term trend underscores the underlying potential and resilience of the Iranian economy. The statistics indicate the gross domestic product (GDP) of Iran from 1960 to 2023, with projections extending until 2028, offering a comprehensive historical and forward-looking perspective. Looking to the near future, various economic models and institutions offer their predictions. According to IMF expectations, the GDP of Iran was anticipated to reach $367.9 billion by the end of 2023. It's important to note that this was an *expectation*, and the actual reported figure by the World Bank was higher at $404.63 billion, suggesting a better-than-anticipated performance or differing methodologies between institutions. For 2024, econometric models predict that the country’s GDP will trend around $388.8 billion. Furthermore, the gross domestic product of Iran is projected to grow by 3.5% in 2024 compared to the previous year, with a nominal figure of $401.357 billion. These projections, while subject to change based on evolving global and domestic conditions, provide a glimpse into the anticipated trajectory of Iran's economy.Understanding Different GDP Metrics
The various figures presented for Iran's GDP highlight the importance of understanding different economic metrics. "Gross Domestic Product (GDP)" is generally defined as the market value of all final goods and services produced within a nation in a given year. When we talk about "current US$" or "nominal GDP," we are referring to GDP calculated at current market prices, which can be influenced by inflation. "Real GDP," on the other hand, adjusts for inflation, providing a more accurate measure of the actual volume of goods and services produced. The "purchasing power index" (PPP) further refines this by accounting for differences in the cost of living and inflation rates between countries, allowing for a more equitable comparison of economic size and living standards. The slight discrepancies in reported figures across different sources (e.g., World Bank vs. IMF expectations, or different per capita figures) often stem from these varying methodologies, base years for constant prices, or the timing of data collection and release. The data from the World Bank collection of development indicators, compiled from officially recognized sources, generally provides a consistent baseline for analysis.Factors Influencing Iran's Economic Trajectory
The economic performance of Iran is shaped by a complex interplay of internal and external factors. While the provided data primarily focuses on the quantitative aspects of GDP, it implicitly reflects the impact of various underlying drivers. Key among these are global oil prices, given the oil sector's significant contribution to GDP, even if it's decreasing. International sanctions have historically played a crucial role, influencing trade, investment, and access to global financial systems. Domestic economic policies, including fiscal and monetary measures implemented by the Central Bank of Iran, are also critical in managing inflation and exchange rates, which are explicitly mentioned as influential factors. For instance, the relationship between exchange rates (ER) and inflation is a constant consideration for policymakers. Furthermore, efforts towards economic diversification, reducing reliance on oil, and fostering growth in non-oil sectors like services and manufacturing are pivotal for long-term stability and sustainable growth. The government's ability to attract foreign and domestic investment, improve the business environment, and address structural economic challenges will continue to shape Iran's GDP trajectory in the coming years. The moderate growth observed in recent years, driven by expansions in services, suggests that these diversification efforts are beginning to bear fruit, contributing to the overall resilience of the Iranian economy.Conclusion: Navigating the Future of Iran's Economy
The analysis of **Iran's GDP in 2023** paints a picture of an economy demonstrating notable resilience and growth, even amidst a challenging global and regional environment. With a nominal GDP of $404.63 billion US dollars and a growth rate of 5.04%, Iran has shown a capacity for expansion, building on consistent growth observed in previous years. The rise in real GDP and GDP per capita indicates tangible improvements in economic output and, to some extent, in the average living standards of its population. Iran's position as the 21st largest economy globally by purchasing power parity further highlights its substantial domestic economic strength. The breakdown of GDP by expenditure reveals a robust private consumption base and significant fixed investment, both crucial- Images Of Joe Rogans Wife
- Faith Jenkins Net Worth 2024
- Chuck Woolery
- Lathe Accident
- Averyleigh Onlyfans Sex
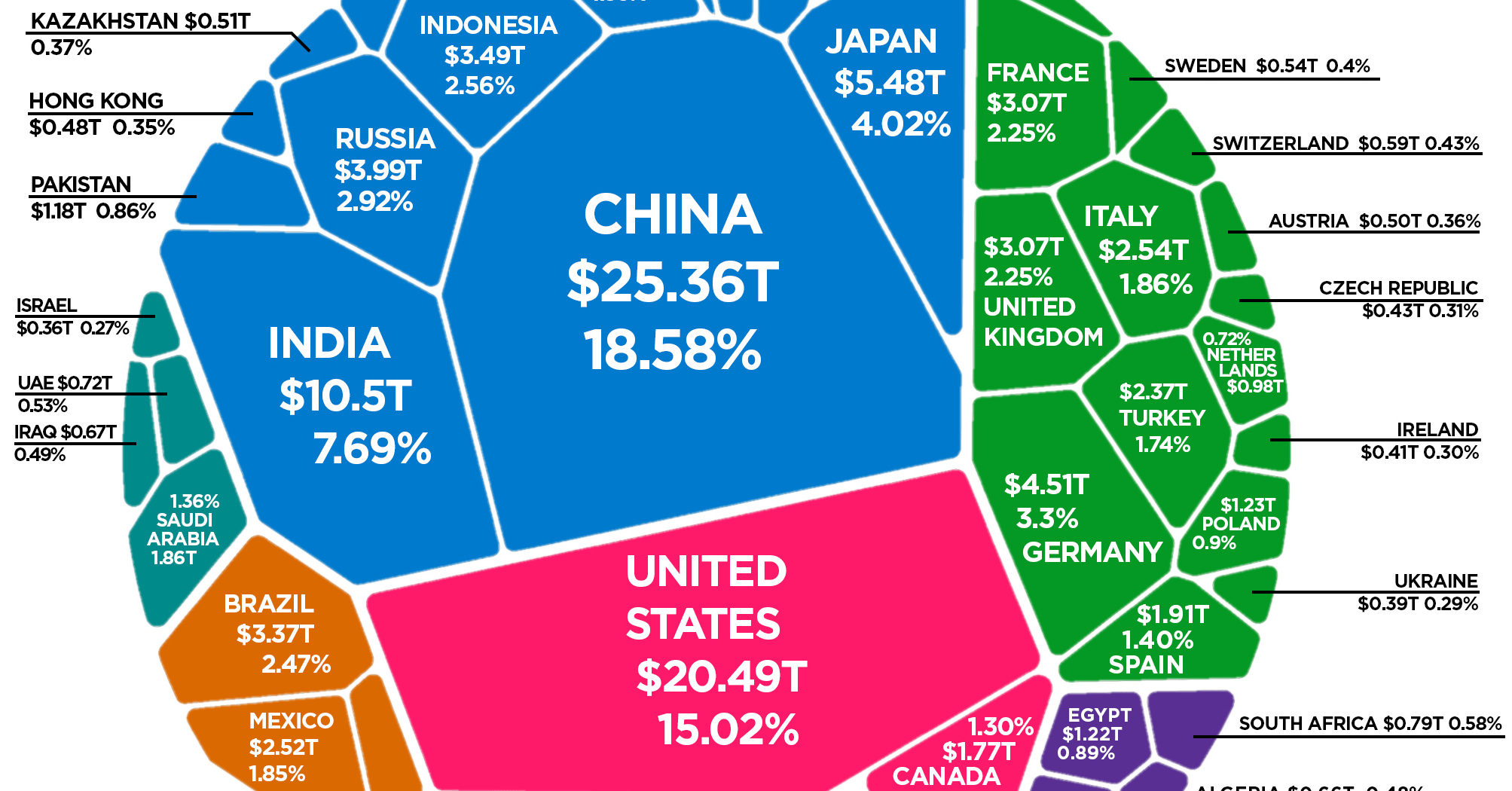
The Composition of the World Economy by GDP (PPP)
/gdp-increase-636251500-c69345ee97ba4db99375723519a2c1bd.jpg)
Real Gross Domestic Product (Real GDP) Definition

The World Economy in One Chart: GDP by Country