Unpacking Iran's GDP: World Bank Data & Economic Outlook
Exploring Iran's GDP data in current US dollars, provided by the World Bank, offers a critical lens into the nation's economic health and its position on the global stage. This comprehensive analysis delves into the intricate details of Iran's gross domestic product, drawing directly from authoritative sources like the World Bank and the Central Bank of Iran. Understanding these figures is not merely an academic exercise; it provides crucial insights for policymakers, business leaders, financial market participants, and anyone interested in the complex dynamics of the Iranian economy.
The economic narrative of Iran is a tapestry woven with rich natural resources, a significant state presence, and the resilience of its people amidst various challenges. Through the detailed reports and indicators compiled by the World Bank, we can gain a clearer picture of the country's economic trajectory, its strengths, and the hurdles it faces. This article aims to demystify the data, offering a clear and accessible overview of Iran's GDP, its constituent sectors, and the broader implications for both domestic prosperity and international relations.
Table of Contents
- Understanding Iran's Economic Landscape Through GDP
- Iran's GDP: Key Figures and Global Standing
- Pillars of the Iranian Economy
- The Iran Economic Monitor: A Vital Resource
- Data Sources and Methodologies
- Exchange Rates and Inflation: Underlying Economic Factors
- Recovery and Future Outlook
- The Broader Impact of Iran's Economic Performance
Understanding Iran's Economic Landscape Through GDP
The Gross Domestic Product (GDP) serves as a fundamental barometer of a nation's economic health, representing the total monetary value of all finished goods and services produced within its borders over a specific period. For a country like Iran, whose economy is often subject to external pressures and internal reforms, understanding its GDP is paramount. The data provided by the World Bank offers a consistent and internationally comparable metric, allowing for meaningful analysis of Iran's economic performance over time and against global benchmarks. This figure reflects the cumulative output of its diverse sectors, from the vast hydrocarbon reserves to its burgeoning services industry and traditional agriculture. It encapsulates the productivity and wealth generation capacity of a nation with a significant population, estimated at 82.8 million people. Analyzing Iran's GDP is not just about numbers; it's about comprehending the livelihood of millions and the strategic decisions that shape their future.The World Bank's Role in Monitoring Iran's Economy
The World Bank plays a crucial role in providing transparent and reliable economic data for countries worldwide, including Iran. Their commitment to producing comprehensive reports like the "Iran Economic Monitor" since April 2016 underscores their dedication to fostering a deeper understanding of the nation's economic dynamics. These reports are not merely compilations of statistics; they are analytical tools that offer updates on key economic developments and policies. By meticulously collecting and synthesizing data from various official sources, including the Central Bank of Iran, national statistical offices, and United Nations publications, the World Bank ensures the integrity and credibility of the information. This ongoing monitoring provides invaluable insights into the trends shaping Iran's economy, making it an indispensable resource for anyone seeking an authoritative perspective on the country's financial landscape. The consistent availability of this data, such as Iran's GDP in current US dollars, allows for robust analysis and informed decision-making.Iran's GDP: Key Figures and Global Standing
Recent data on Iran's GDP provides a snapshot of its economic size and its relative position in the global economy. According to official data from the World Bank, the gross domestic product (GDP) in Iran was worth 404.63 billion US dollars in 2023. This figure, specifically reported as 404,625,655,205 USD in 2023 by the World Bank collection of development indicators, compiled from officially recognized sources, highlights the significant scale of the Iranian economy. While substantial, it also places Iran's economic contribution in a broader context. The GDP value of Iran represents approximately 0.38 percent of the world economy. This percentage, though seemingly small, indicates Iran's presence as a notable, albeit not dominant, player on the global economic stage. Understanding this proportion helps in contextualizing trade relationships, investment flows, and geopolitical influences tied to economic power. The consistency and reliability of the World Bank's data are crucial for such comparative analyses, providing a trusted foundation for economic discussions.Historical Context and Recent Trends
Examining Iran's GDP over time reveals a dynamic economic trajectory. For instance, Iran’s GDP in 2019/20 was estimated at US$463 billion. Comparing this to the 2023 figure of $404.63 billion US dollars indicates a fluctuation, reflecting the impact of various internal and external factors on the economy. These factors can range from global oil price volatility, which significantly impacts a hydrocarbon-dependent economy, to international sanctions and domestic policy decisions. The "Iran Economic Monitor, Spring 2024" and previous revisions, such as the "2022 revision" from the United Nations (UN), provide a continuous narrative of these shifts. Despite challenges, Iran’s economy continued its gradual recovery in 2021/22 following a rebound in domestic and external demand. This suggests a degree of resilience and adaptability within the economic system. Analyzing these trends, supported by calculations from the Central Bank of Iran and World Bank staff, helps in forecasting future performance and identifying areas of potential growth or vulnerability. The ability to track Iran's GDP through these historical data points is vital for understanding its economic evolution.Pillars of the Iranian Economy
With a population of 82.8 million people, Iran’s economy is characterized by a blend of traditional strengths and evolving sectors. The primary pillars include the hydrocarbon sector, which remains the cornerstone due to Iran's vast oil and natural gas reserves. This sector not only provides significant export revenues but also fuels domestic industries. Alongside hydrocarbons, the agriculture sector plays a vital role, supporting a substantial portion of the population and contributing to food security. Despite its traditional nature, agriculture is subject to environmental factors and technological advancements. The services sector has also seen considerable growth, encompassing a wide array of activities from retail and tourism to finance and information technology. Beyond these, there is a noticeable state presence in manufacturing and financial services, indicating a significant government influence on key economic activities. This mixed economic structure, with its blend of state control and private enterprise, shapes the overall performance of Iran's GDP. The interplay between these sectors dictates the country's economic stability and growth potential.Challenges and Contractions
Despite the inherent strengths of its core sectors, Iran's economy is not without its significant challenges, which can lead to contractions in Iran's GDP. One prominent issue highlighted in economic reports is the impact of water and energy shortages. These critical resource constraints have directly led to a contraction of the agriculture and industry sectors. Water scarcity, exacerbated by climate change and inefficient management, directly affects agricultural output, impacting food supply and rural livelihoods. Similarly, energy shortages can cripple manufacturing and industrial production, leading to reduced output and economic slowdowns. These internal structural issues, combined with external pressures such as international sanctions, create a complex environment for economic growth. Understanding these challenges is crucial for a holistic view of Iran's economic landscape, as they directly influence the nation's capacity for sustainable development and the overall trajectory of Iran's GDP. Addressing these fundamental issues is key to unlocking Iran's full economic potential and ensuring long-term stability.The Iran Economic Monitor: A Vital Resource
The "Iran Economic Monitor" (IEM) is an indispensable publication produced by the World Bank’s Global Practice for Macroeconomics, Trade & Investment. This comprehensive report provides regular updates on key economic developments and policies within Iran, offering a nuanced understanding of the country's financial and economic landscape. Since its inception in April 2016, the IEM has served as a consistent and reliable source of information, meticulously detailing economic trends, policy shifts, and their implications. It goes beyond mere statistics, delving into the underlying factors that drive economic change, such as exchange rates and inflation, which are crucial for assessing the real value of Iran's GDP and the purchasing power of its currency. The IEM's commitment to providing an in-depth, expert analysis makes it a cornerstone for anyone seeking to understand the complexities of the Iranian economy, ensuring that the insights provided are both timely and accurate.Target Audience and Scope
The "Iran Economic Monitor" is specifically designed for a wide and diverse audience, reflecting the broad interest in Iran's economic performance. This includes policy makers, who rely on the report for informed decision-making regarding national economic strategies; business leaders, who use the insights to navigate investment opportunities and risks; and financial market participants, who need up-to-date information to make sound investment choices. Furthermore, the report caters to the broader community of analysts and professionals engaged on Iran, providing them with authoritative data and expert analysis. The scope of the IEM is extensive, covering everything from the overall economy to financial markets and indicators of human welfare and development. This holistic approach ensures that the report offers a comprehensive picture of Iran's economic health, extending beyond just Iran's GDP figures to encompass the socio-economic impacts of economic policies and trends. Its wide appeal underscores the importance of transparent and accessible economic data for a variety of stakeholders.Data Sources and Methodologies
The reliability of any economic analysis hinges on the quality and integrity of its underlying data. The World Bank's reporting on Iran's GDP and other economic indicators is built upon a foundation of rigorously compiled information from officially recognized and trusted sources. Key among these are the Central Bank of Iran, which provides crucial monetary and financial statistics, and national statistical offices, responsible for collecting and disseminating demographic and economic survey data. Additionally, the World Bank incorporates information from various United Nations (UN) publications, such as "Population and vital statistics report (various years)" and "Census reports and other statistical publications." The "International Database" from the United States Census Bureau also contributes to the comprehensive dataset. This multi-source approach, combined with the World Bank's robust methodologies for data processing and analysis, ensures the accuracy and comparability of the reported figures, including Iran's GDP in current US dollars. Such meticulous compilation is essential for maintaining the E-E-A-T principles of expertise, authoritativeness, and trustworthiness in economic reporting.Exchange Rates and Inflation: Underlying Economic Factors
While Iran's GDP provides a headline figure of economic output, its true value and the economic well-being of its citizens are significantly influenced by underlying macroeconomic factors such as exchange rates (ER) and inflation. These elements are meticulously tracked and analyzed in reports like the "Iran Economic Monitor," often depicted in figures illustrating their trends. High inflation can erode purchasing power, making goods and services more expensive for the average Iranian, even if the nominal GDP appears stable. Similarly, fluctuations in exchange rates directly impact the value of Iran's GDP when converted to US dollars, affecting its global comparability and the cost of imports and exports. For an economy heavily reliant on hydrocarbon exports priced in US dollars, the exchange rate is a critical determinant of national income. The interplay between these factors can either amplify or dampen the effects of economic growth or contraction. Therefore, a comprehensive understanding of Iran's economic health necessitates a close examination of these crucial monetary indicators, which are often the result of complex policy decisions and external pressures.Recovery and Future Outlook
Despite facing significant headwinds, Iran's economy has demonstrated a degree of resilience and a gradual path towards recovery in recent years. Following periods of contraction, Iran’s economy continued its gradual recovery in 2021/22, a trend attributed to a rebound in both domestic and external demand. This recovery suggests an underlying capacity for growth, even amidst challenging circumstances. While specific forecasts for future Iran's GDP are subject to numerous variables, including global oil prices, geopolitical developments, and domestic policy reforms, the World Bank's ongoing monitoring provides a basis for cautious optimism. The "Iran Economic Monitor, Spring 2024" will likely offer updated projections and analyses, reflecting the latest economic data and policy shifts. Sustaining this recovery will depend on addressing structural issues like water and energy shortages, fostering a more robust private sector, and navigating international relations. The trajectory of Iran's GDP in the coming years will be a critical indicator of the success of these efforts and the overall stability of the nation.The Broader Impact of Iran's Economic Performance
The performance of Iran's GDP extends far beyond mere statistical figures; it has profound implications across various facets of national and international life. A strong and stable economy, as reflected in a growing GDP, can lead to improved human welfare and development indicators, including better access to education, healthcare, and employment opportunities for the 82.8 million people. Conversely, economic contraction or stagnation can exacerbate social challenges and reduce living standards. From a financial perspective, the health of Iran's economy directly impacts its financial markets, influencing investment decisions, currency stability, and the overall business climate. For the international community, Iran's economic trajectory holds significant geopolitical weight, affecting regional stability, energy markets, and global trade dynamics. The World Bank's comprehensive reports, which span from the "economy to financial markets to indicators of human welfare and development," underscore this interconnectedness. Therefore, understanding Iran's GDP is not just about economic numbers; it's about grasping the intricate web of factors that shape the lives of its citizens and its role in the global arena.Conclusion
The journey through Iran's GDP data, meticulously compiled and analyzed by the World Bank, offers an invaluable perspective on the nation's economic landscape. From the estimated US$463 billion in 2019/20 to the 404.63 billion US dollars reported in 2023, these figures paint a picture of an economy characterized by its hydrocarbon wealth, agricultural base, and a growing services sector, all under a noticeable state presence. Despite facing significant challenges like water and energy shortages, which have led to contractions in key sectors, the Iranian economy has shown signs of gradual recovery. The "Iran Economic Monitor" stands as a testament to the World Bank's commitment to providing transparent, authoritative, and trustworthy insights for a diverse audience, from policymakers to financial market participants. By relying on robust data sources and methodologies, the World Bank ensures that its analysis of Iran's GDP and other indicators remains a crucial resource for understanding the country's economic trajectory and its broader impact on human welfare and global dynamics. We encourage you to delve deeper into the World Bank's publications, such as the "Iran Economic Monitor," for the most current and detailed insights. What are your thoughts on Iran's economic future? Share your perspectives in the comments below, and consider sharing this article to foster a wider discussion on this important topic.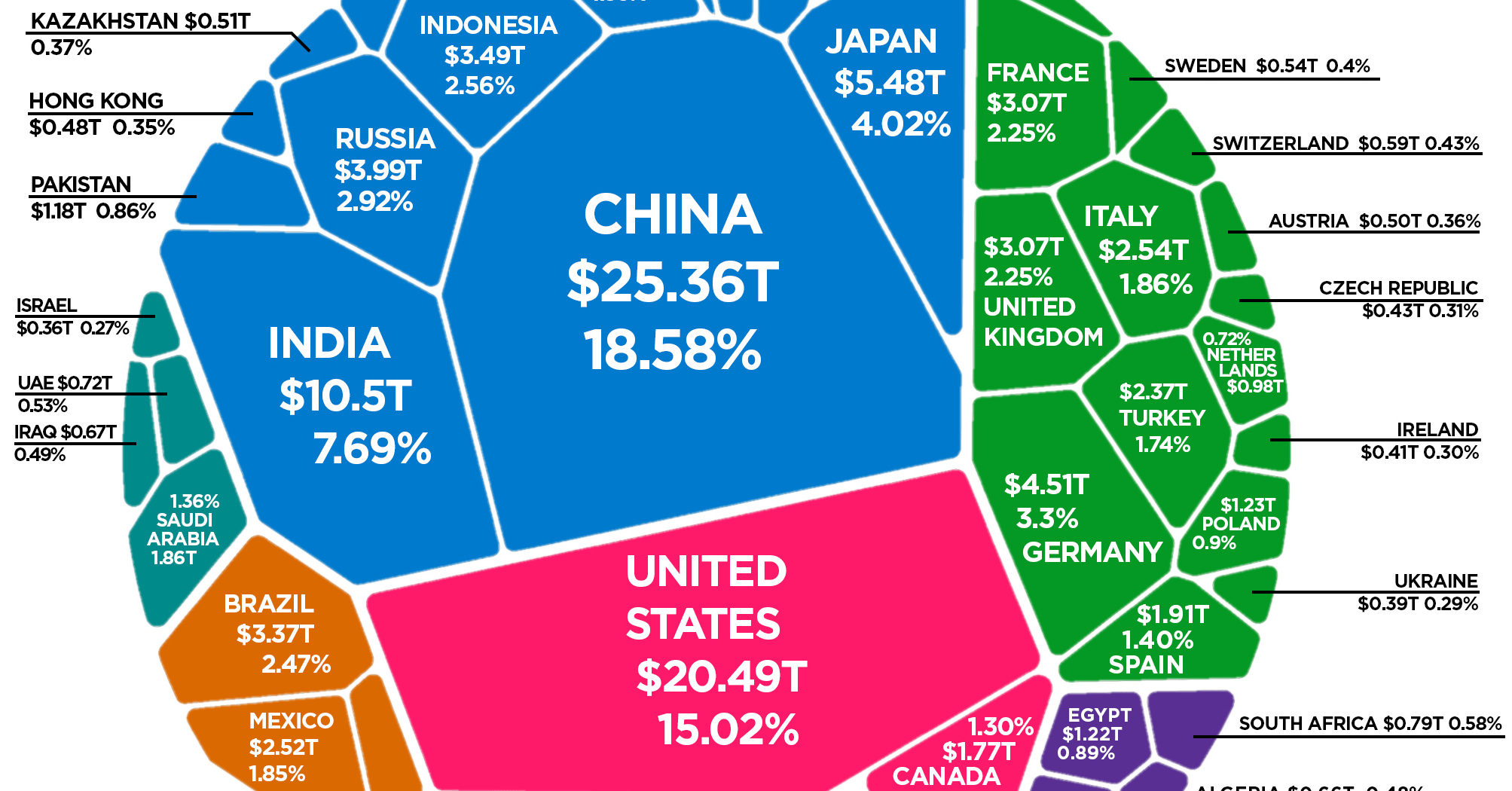
The Composition of the World Economy by GDP (PPP)
/gdp-increase-636251500-c69345ee97ba4db99375723519a2c1bd.jpg)
Real Gross Domestic Product (Real GDP) Definition

The World Economy in One Chart: GDP by Country