Iran's Economy In 2012: A Deep Dive Into GDP Fluctuations
Understanding a nation's economic health often begins with its Gross Domestic Product (GDP). For Iran, 2012 represented a pivotal year, marked by significant shifts and a complex economic landscape. This article delves into the specifics of Iran's GDP in 2012, examining the figures, their implications, and the broader context that shaped the nation's financial standing during this period. We will explore how Iran's economy performed, its ranking on the global stage, and what these numbers tell us about the challenges and resilience faced by the country.
The year 2012 holds particular significance for Iran's economic trajectory. While often highlighted for its geopolitical complexities, the underlying economic data provides a clearer picture of the real impact on its citizens and its position in the world economy. By dissecting the various components of its GDP, including per capita figures and historical trends, we can gain valuable insights into the forces at play and better comprehend the economic narrative of Iran.
Table of Contents
- Understanding GDP: A Foundational Overview
- Iran GDP 2012: The Headline Figures
- A Peak Year Amidst Challenges: Iran GDP 2012
- The Definition of GDP: What the Numbers Mean
- Historical Context and Trends Leading Up to 2012
- Economic Factors and Influences in 2012
- Post-2012 Economic Recovery and Fluctuations
- Methodologies and Data Sources for Iran GDP
- The Bertelsmann Stiftung Transformation Index 2012 Perspective
- Conclusion: Navigating Iran's Economic Landscape
Understanding GDP: A Foundational Overview
Before diving into the specific figures for **Iran GDP 2012**, it's essential to grasp what Gross Domestic Product (GDP) truly represents. GDP is a fundamental measure of a nation's economic output. At its core, Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is defined as the market value of all final goods and services produced within a nation's borders in a given year. This comprehensive metric provides a snapshot of the economy's size and health. When looking at "GDP at purchaser's prices," it's the sum of gross value added by all resident producers in the economy, plus any product taxes, minus any subsidies not included in the value of the products. This definition ensures that the calculation reflects the total economic activity occurring within the country. Understanding these foundational principles is crucial for interpreting the economic data, especially when discussing a complex year like **Iran GDP 2012**.Iran GDP 2012: The Headline Figures
The year 2012 presented a multifaceted picture for Iran's economy, with various data points offering different perspectives on its performance. According to one set of figures, the GDP in 2012 was €328,159 million, equivalent to approximately $421,882 million (or $421.882 billion). This figure placed Iran at number 29 in the ranking of GDP among the 196 countries for which data was published. However, it's important to note that other reputable sources, such as data provided by the World Bank, indicated a different, and significantly higher, figure for **Iran GDP 2012**. Specifically, Iran's GDP reached an all-time high of $644.02 billion USD in 2012, with another data point confirming $644.04 billion USD on December 31, 2012. This discrepancy highlights the importance of understanding the methodologies and sources behind economic data, as different calculations (e.g., current prices, constant prices, various exchange rates, or specific institutional estimates) can lead to varied reported values. Despite these variations, the year 2012 stands out for Iran's economy.Absolute Value and Global Ranking
The absolute value of GDP in Iran saw a notable drop of €121,238 million, or approximately $203,548 million, with respect to 2011. This decline indicates significant economic pressures impacting the country during this period. Despite this contraction from the previous year, the World Bank data suggests that 2012 was still a peak year in terms of nominal GDP, reaching an all-time high of $644.02 billion USD. This seemingly contradictory information (a drop from 2011 but an "all-time high" in the broader historical context) can be reconciled by understanding that the "all-time high" refers to the entire period from 1960 to 2023, while the drop is a year-over-year comparison. The ranking of 29th globally among 196 countries for the $421.882 billion figure demonstrates Iran's substantial economic size on the world stage, even amidst a period of contraction. Countries are typically sorted by nominal GDP estimates from financial and statistical institutions, calculated at market or government official exchange rates, which influences their global standing.GDP Per Capita in 2012
Beyond the overall economic size, GDP per capita offers crucial insights into the average economic well-being of a nation's citizens. In 2012, the GDP per capita of Iran was €4,316, or approximately $5,548. This figure represented a significant decrease of €1,664 ($2,774) compared to 2011, when it stood at €5,980 ($8,322). The substantial drop in per capita GDP indicates that the economic contraction was directly felt by the population, leading to a reduction in average income and purchasing power. This metric is particularly important for understanding the impact of economic policies and external factors on the daily lives of individuals within Iran. The decline in both absolute GDP and GDP per capita underscores the challenging economic environment of 2012 for the nation.A Peak Year Amidst Challenges: Iran GDP 2012
Despite the year-over-year decline in some reported figures, 2012 remains a significant year for Iran's economy in a broader historical context. As highlighted by World Bank data, GDP in Iran averaged $181.91 billion USD from 1960 until 2023. Within this extensive timeline, the year 2012 stands out, reaching an all-time high of $644.02 billion USD. This peak, further supported by the figure of $644.04 billion USD on December 31, 2012, suggests that even with a reported drop from 2011 in certain metrics, the overall economic output for **Iran GDP 2012** was remarkably high when viewed against decades of historical performance. This juxtaposition of an "all-time high" with a year-on-year decline points to the complexity of Iran's economic situation, likely influenced by various internal and external factors that peaked its nominal GDP while simultaneously creating immediate challenges.The Definition of GDP: What the Numbers Mean
To truly appreciate the data surrounding **Iran GDP 2012**, it's vital to have a clear understanding of what Gross Domestic Product (GDP) entails. As previously mentioned, GDP is the market value of all final goods and services from a nation in a given year. This definition helps us understand the scope of what these figures represent. When we talk about "GDP at purchaser's prices," we are referring to the sum of gross value added by all resident producers in the economy, plus any product taxes, and minus any subsidies not included in the value of the products. This comprehensive measure captures the total economic output within a country's borders, regardless of who owns the production factors. It includes everything from agricultural output and industrial production to services, reflecting the overall economic activity. Therefore, when we analyze the substantial figures for **Iran GDP 2012**, we are looking at the cumulative value of every economic transaction that contributed to the nation's wealth that year.Historical Context and Trends Leading Up to 2012
Understanding the economic landscape of **Iran GDP 2012** requires a look at its historical performance. Economic data for Iran, including GDP, has been estimated by the World Bank since 1960 in nominal terms and since 1990 in Purchasing Power Parity (PPP) terms, at both current and constant prices. This long-term perspective reveals that Iran's GDP has averaged $181.91 billion USD from 1960 until 2023. The journey to the 2012 peak was not linear. For instance, the record low for Iran's GDP was $4.20 billion USD in 1960, illustrating the immense growth and transformation the economy underwent over several decades. The period leading up to 2012 saw various phases of growth and contraction, influenced by global oil prices, domestic policies, and international relations. The significant jump to an all-time high in 2012, despite a reported decline from 2011 in some metrics, suggests that the preceding years likely built up to a substantial nominal valuation, possibly driven by high oil revenues before the full impact of sanctions took hold, or by specific accounting methods for that year. Analyzing these historical data points allows for a more informed interpretation of the unique position of **Iran GDP 2012** within its broader economic narrative.Economic Factors and Influences in 2012
The year 2012 was particularly challenging for Iran's economy, marked by a confluence of internal and external pressures. While the nominal GDP reached an all-time high in USD terms, the reported drop in absolute value and per capita GDP from 2011 highlights the immediate difficulties. A primary external factor was the intensification of international sanctions, particularly those targeting Iran's oil exports and its central bank. These sanctions severely restricted Iran's ability to sell its crude oil, which is a major source of government revenue and foreign exchange. The inability to easily transfer funds also complicated international trade and financial transactions. Domestically, the economy faced challenges such as high inflation, unemployment, and structural issues. The Bertelsmann Stiftung’s Transformation Index (BTI) 2012 report, which provides a global assessment of transition processes, likely shed light on the governance and economic management aspects within Iran during this period. While the specific score for Iran in the BTI 2012 is not provided in the data, such assessments typically evaluate factors like economic stability, market organization, and welfare regimes, all of which would have influenced the economic performance and the figures for **Iran GDP 2012**. The combination of these internal fragilities and external pressures created a volatile environment for Iran's economic output and the well-being of its population.Post-2012 Economic Recovery and Fluctuations
The economic trajectory of Iran did not stabilize after 2012; rather, it continued to experience significant fluctuations, demonstrating both periods of decline and impressive recovery. While **Iran GDP 2012** marked an all-time high in nominal USD terms, the subsequent years presented new challenges and opportunities. Tracking Iran's GDP historical data and exploring predictions, news, and related indicators is crucial to better navigate the global economy and understand the country's economic resilience. The provided data gives us glimpses into the more recent past and future projections, showing how the economy has adapted or struggled in the years following that peak.Recent GDP Trends (2019-2022)
Looking at more recent data, Iran's GDP has continued its volatile path. For instance, Iran's GDP for 2020 was $239.74 billion USD, representing a 15.48% decline from 2019. This significant drop can be attributed to various factors, including renewed sanctions and the global economic impact of the COVID-19 pandemic. However, the economy showed signs of recovery in the subsequent year: Iran's GDP for 2021 was $359.10 billion USD, marking a substantial 49.79% increase from 2020. This rebound suggests a degree of resilience, possibly driven by adaptations to sanctions or a recovery in certain sectors. The GDP growth rate for 2020 was 3.33%, a 6.4% increase from 2019, indicating some underlying growth despite the nominal GDP decline. For 2021, the growth rate was 4.72%, a 1.39% increase from 2020. However, the growth rate for 2022 was 3.78%, a 0.94% decline from 2021, showing that sustained, strong growth remains a challenge. These figures, though far from the nominal peak of **Iran GDP 2012**, illustrate the dynamic and often unpredictable nature of Iran's economic performance.GDP Outlook for 2024
Projections for Iran's economy continue to show movement. The GDP figure in 2024 is projected to be €370,921 million, or approximately $401,357 million. This would place Iran at number 41 in the ranking of GDP among the 196 countries, a drop from its 29th position in 2012. The absolute value of GDP in Iran is projected to rise by €26,222 million ($28,537 million) with respect to 2023, indicating an expected increase in economic output. Furthermore, the GDP per capita of Iran in 2024 is projected to be €4,094 ($4,430), which is €290 ($315) higher than in 2023, when it was €3,804 ($4,115). These forward-looking figures suggest continued, albeit modest, growth in the near term, demonstrating that Iran's economy is constantly evolving, attempting to navigate both internal and external pressures.Methodologies and Data Sources for Iran GDP
The accuracy and comparability of GDP data heavily rely on the methodologies used and the reliability of the sources. For Iran's GDP, data is primarily provided by the World Bank, offering estimates since 1960 in nominal terms and since 1990 in PPP terms, at both current and constant prices. Gross Domestic Product (GDP) data for the Islamic Republic of Iran (mktgdpira646nwdb) from 1960 to 2023 is available for exploration and download, indicating comprehensive historical records. The annual percentage growth rate of GDP is based on market prices using constant local currency, and aggregates are based on constant 2010 U.S. dollars. The fact that countries are sorted by nominal GDP estimates from financial and statistical institutions, calculated at market or government official exchange rates, explains potential variations in reported figures. These robust methodologies and long-term data collection efforts by institutions like the World Bank lend credibility to the figures, allowing for a detailed analysis of economic performance, including the complex picture of **Iran GDP 2012**.The Bertelsmann Stiftung Transformation Index 2012 Perspective
Beyond raw economic figures, qualitative assessments provide crucial context. The Bertelsmann Stiftung’s Transformation Index (BTI) 2012 report offers a global assessment of transition processes, evaluating countries on various dimensions including political and economic transformation. While specific scores for Iran in the BTI 2012 are not detailed in the provided data, such a report would analyze the quality of governance, the state of the market economy, and the extent of social justice. The BTI uses a scoring system, typically from 1 (lowest) to 10 (highest), to gauge performance in these areas. For a country like Iran, facing significant international sanctions and internal economic pressures in 2012, the BTI would have assessed how effectively the government managed its economy, fostered market structures, and provided for its citizens. This broader perspective helps to contextualize the nominal GDP figures, revealing the underlying structural and governance challenges that might have influenced the economic downturn from 2011 to 2012, even as the nominal GDP reached an all-time high in a longer historical view.Conclusion: Navigating Iran's Economic Landscape
The analysis of **Iran GDP 2012** reveals a complex economic narrative. While some figures indicated a significant year-on-year drop in both absolute GDP and per capita income, other data, particularly from the World Bank, highlighted 2012 as a remarkable year, reaching an all-time high nominal GDP of over $644 billion USD. This duality underscores the intricate interplay of internal economic dynamics, global market forces, and the profound impact of international sanctions. The year serves as a powerful case study in economic resilience and vulnerability, demonstrating how a nation can achieve a historical peak in nominal terms while simultaneously grappling with immediate contraction and a decline in living standards. Understanding Iran's economic journey, from its historical averages to its recent fluctuations and future projections, is crucial for anyone interested in global economics or the specific challenges faced by nations under significant external pressure. The data, consistently provided by reputable sources like the World Bank, offers a valuable resource for tracking these trends. We hope this deep dive into **Iran GDP 2012** has provided you with valuable insights into a pivotal period for the country's economy. What are your thoughts on the factors that shaped Iran's economic performance in 2012 and beyond? Share your comments below, or explore other articles on our site to further your understanding of global economic trends.- Maria Burton Carson
- Claire Anne Callens
- Prince William Reportedly Holds A Grudge Against Prince Andrew
- Xxbritz
- Rebecca Lynn Howard Husband
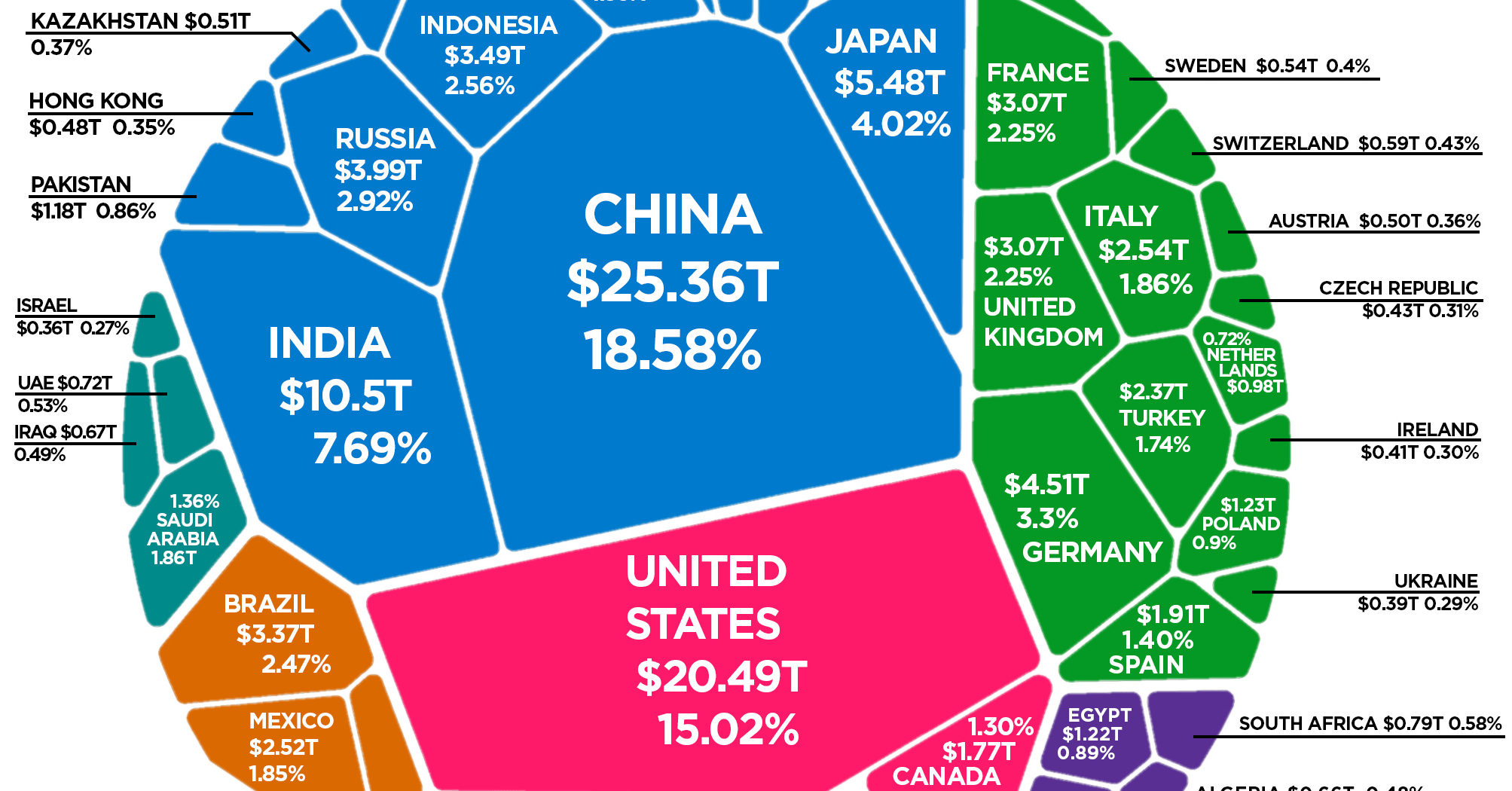
The Composition of the World Economy by GDP (PPP)
/gdp-increase-636251500-c69345ee97ba4db99375723519a2c1bd.jpg)
Real Gross Domestic Product (Real GDP) Definition

The World Economy in One Chart: GDP by Country