Unveiling Iran's Population Dynamics: Growth, Trends & Future
Table of Contents
- Understanding the Scale: Iran's Place in Global Demographics
- A Look Back: Historical Trajectories of Iran's Population
- The Recent Surge: Iran's Population in the 21st Century
- Density and Distribution: Where Do Iranians Live?
- Shifting Tides: Birth Rates and Demographic Shifts
- The Iranian Diaspora: A Global Presence
- Demographic Implications: Economic and Social Considerations
- Conclusion: Navigating Iran's Demographic Landscape
Understanding the Scale: Iran's Place in Global Demographics
When we consider the global demographic landscape, Iran holds a significant position. As mentioned, the population in Iran is equivalent to 1.12% of the total world population. This percentage, while seemingly small, places Iran at number 17 in the list of countries and dependencies by population. This ranking signifies Iran's substantial human capital and its considerable demographic footprint on the world map. For context, it means that out of every hundred people on Earth, more than one is an Iranian. This scale is particularly noteworthy given Iran's vast land area, which totals 1,628,550 km² (628,786 sq mi). The sheer size of the country, approximately 75 times larger than Israel, provides ample space for its populace, though as we will explore, the distribution of this population is far from uniform. The country's unique geographical features, ranging from deserts to mountains and fertile plains, contribute to varied settlement patterns and population densities across its expansive territory.A Look Back: Historical Trajectories of Iran's Population
The demographic history of Iran is marked by distinct phases, showcasing periods of stagnation followed by explosive growth. For a significant period, from 1880 till 1920, the population of Iran remained remarkably stable, hovering at 10 million or below. This era was characterized by various factors including political instability, limited healthcare, and agricultural economies that constrained rapid population expansion. However, the tide began to turn in the 20th century. From 1920 onwards, Iran's population started to increase steadily. By 1955, the population rate had reached 20 million, effectively doubling in just 35 years. This period coincided with the beginnings of modernization efforts, improved public health, and greater political centralization. The most dramatic increase, however, occurred in the latter half of the 20th century. According to statistics, the population experienced a drastic surge, reaching 50 million in 1985. This rapid growth continued, with the population reaching about 80 million by 2016. The period between 1960 and 2023 is particularly striking: the number of inhabitants in Iran soared from 21.91 million to 90.61 million, an astonishing increase of 313.6% over 63 years. This contrasts sharply with the global population increase of 165.9% over the same period, underscoring the exceptional growth trajectory of the population in Iran. The year 2015 notably saw the highest annual increase, at 5.58%, a testament to the momentum of this demographic boom.The Recent Surge: Iran's Population in the 21st Century
The early decades of the 21st century have seen the population in Iran continue its upward trend, albeit with emerging signs of a slowdown. The figures from recent years and projections for the near future provide a detailed snapshot of this ongoing demographic evolution.Current Population Snapshot
As of November 2024, Iran's population is estimated to be around 91.5 million. This figure is consistent with data from the UN, which also reported the population of Iran as 91.5 million for 2024. Looking slightly ahead, the total population in Iran is projected at 91,567,738, or approximately 91.57 million people, for the year 2024 based on midyear estimates. For 2025, projections indicate a continued, albeit moderated, increase. The population of Iran is projected at 92,417,681, or 92.42 million, as of July 1, 2025. More granular daily data from May 15, 2025, estimates the population at 92,311,974. These figures highlight the ongoing growth, pushing the country closer to the 92 million mark. It's important to note that these are de facto population estimates, meaning they count all residents regardless of legal status or citizenship.Growth Rates and Urbanization Trends
While the population in Iran continues to grow, the pace of this growth has begun to moderate. The current annual growth rate is reported at 0.859%, with a slightly higher projection of 0.86% per year for May 2025. This rate indicates a significant slowdown compared to the rapid increases observed in the late 20th century. For instance, total population for Iran in 2023 was 90,608,707, marking a 1.21% increase from 2022. Similarly, the total population for Iran in 2022 was 89,524,246, also a 1.21% increase from 2021. The slight decrease in the annual growth rate from 1.21% to around 0.86% signals a clear demographic shift. A key characteristic of the population in Iran is its high degree of urbanization. A significant 73.32% of the population is urban, translating to an estimated 67,760,281 people living in urban areas in 2025. This high urbanization rate reflects a global trend but also points to internal migration patterns within Iran, as people move from rural areas to cities in search of economic opportunities and better services. This concentration of people in urban centers has profound implications for infrastructure development, resource management, and social planning.Density and Distribution: Where Do Iranians Live?
Understanding the population in Iran also requires an examination of its density and how people are distributed across its vast landmass. The total land area of Iran is 1,628,550 km² (628,786 sq mi), which provides a large canvas for its inhabitants. The population density in Iran is currently estimated at 57 people per km² (147 people per mi²). More specifically, as of June 2025, the density is projected to be 53.9 people per square kilometer (139.7/mi²). This density is calculated by dividing the permanently settled population by the total area of the country, which includes both land and water areas within international boundaries. Compared to many other populous nations, Iran's overall population density is relatively moderate. However, this average figure masks significant regional variations. Much of Iran's terrain consists of arid deserts and rugged mountain ranges, which are sparsely populated. The majority of the population is concentrated in the western and northern parts of the country, particularly in the fertile plains, river valleys, and coastal regions, where access to water and arable land is more readily available. Major cities like Tehran, Mashhad, Isfahan, and Tabriz serve as significant urban hubs, attracting large numbers of people and contributing to higher localized densities. The high urban population percentage (over 73%) further underscores this concentration, indicating that while the overall density might seem low, urban centers are experiencing considerable demographic pressure. This uneven distribution poses challenges for regional development, resource allocation, and the provision of services.Shifting Tides: Birth Rates and Demographic Shifts
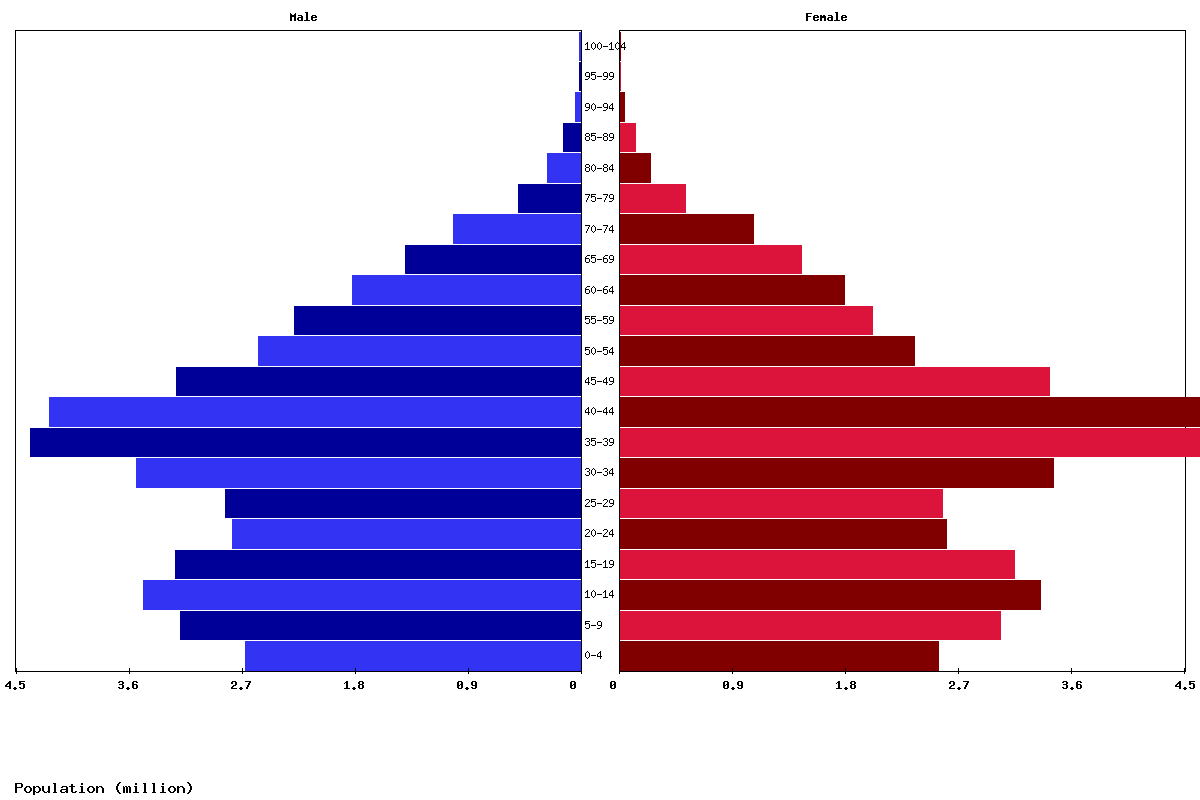
The trajectory of the population in Iran is increasingly influenced by changing birth rates, which have seen a significant decline in recent years. This demographic shift is a critical factor in understanding the country's future population dynamics. Iran's population increased dramatically during the later half of the 20th century, largely due to high birth rates and improvements in healthcare. However, in recent years, Iran's birth rate has dropped significantly. This decline is a complex phenomenon, likely influenced by factors such as increased education among women, greater access to family planning, urbanization, changing socio-economic aspirations, and the rising cost of living. Studies project that Iran's rate of population growth will continue to slow. This slowing is not just a theoretical projection; it is already evident in the decreasing annual growth rates observed between 2021-2023 (1.21%) and the current projections for 2024-2025 (around 0.86%). The daily statistics further illustrate this trend. As of May 15, 2025, Iran is projected to experience approximately 3,083 births per day, alongside 1,228 deaths per day. While births still significantly outnumber deaths, the rate of births has decreased from historical highs. This trend suggests that Iran is moving towards a more mature demographic profile, similar to many developed nations, where birth rates fall below replacement levels over time. Such a shift has profound implications for the age structure of the population, potentially leading to an aging society in the coming decades, with a smaller proportion of working-age individuals supporting a larger elderly population. This demographic transition presents both opportunities and challenges for the Iranian government in terms of social welfare, healthcare, and economic planning.The Iranian Diaspora: A Global Presence
Beyond the borders of the country, the population in Iran also extends to a significant global diaspora. This outward migration has played a crucial role in shaping Iran's demographic profile, particularly in the aftermath of major political events. Following the 1979 Iranian Revolution, a sizeable number of Iranians emigrated to other countries. This movement was driven by a variety of factors, including political changes, economic uncertainties, and social transformations within Iran. It is estimated that over 5 million Iranians have emigrated, establishing communities across North America, Europe, and other parts of the Middle East. This diaspora represents a significant demographic and cultural extension of Iran, maintaining ties with their homeland through various means, including remittances, cultural exchange, and political advocacy. The existence of such a large diaspora means that the true global reach of the Iranian people extends far beyond the country's geographical boundaries. While these individuals are no longer counted within the de facto population of Iran, their connection to the country remains strong. The diaspora contributes to a broader understanding of Iranian culture and society on a global scale, and their experiences often reflect the complex socio-political dynamics within Iran itself. The flow of people, ideas, and resources between Iran and its diaspora continues to be an important, albeit often unquantified, aspect of the broader Iranian demographic story.Demographic Implications: Economic and Social Considerations
The size, growth, and distribution of the population in Iran have far-reaching implications for its economy, social structures, and future development. These demographic trends are not merely numbers; they represent the collective potential, needs, and challenges of a nation.Beyond Numbers: Daily Life and Demographic Realities
The daily demographic realities in Iran, such as the approximately 3,083 births and 1,228 deaths per day as of May 2025, illustrate the continuous renewal and natural churn of the population. These figures are vital for planning public services, from maternity wards to cemeteries, and for understanding the ongoing pressures on infrastructure. The high percentage of urban dwellers (73.32%) means that cities bear the brunt of population growth, demanding robust urban planning, housing development, transportation networks, and environmental management. Economically, a large and relatively young population can be a significant asset, providing a substantial labor force and a consumer base. However, it also requires sustained economic growth to create sufficient jobs and opportunities. Iran's nominal Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is $418 billion, ranking it 36th globally. While this is a substantial economy, the per capita GDP is influenced by the large population, highlighting the need for continued economic diversification and productivity enhancements to improve living standards for its growing populace. The slowing birth rate, while potentially easing pressure on immediate job creation, signals a future challenge related to an aging workforce and increased dependency ratios.Future Projections and Policy Challenges
Studies project that Iran's rate of population growth will continue to slow. This demographic transition presents both opportunities and significant policy challenges. An aging population, for instance, will place greater demands on social security systems, healthcare services, and elder care facilities. The government will need to adapt its policies to ensure the well-being of its older citizens while simultaneously fostering an environment that encourages sustainable economic growth and innovation among its younger generations. Furthermore, the significant increase in the population in Iran from 21.91 million in 1960 to over 90 million today means that a large proportion of the current population grew up during periods of rapid expansion. This generation will soon be entering or already is in its prime working years, offering a demographic dividend if adequately skilled and employed. However, if economic opportunities do not keep pace with the growing labor force, it could lead to social unrest and brain drain, potentially exacerbating the diaspora trend. Therefore, understanding and proactively addressing these demographic shifts is paramount for Iran's long-term stability and prosperity.Conclusion: Navigating Iran's Demographic Landscape
The population in Iran is a multifaceted and ever-evolving subject, characterized by a history of dramatic growth, a current phase of moderation, and a future marked by significant demographic shifts. From its historical plateau at 10 million to its current standing as the 17th most populous nation with over 92 million inhabitants, Iran's demographic journey is a testament to profound societal transformations. The country's high urbanization rate, coupled with a moderating birth rate, signals a transition towards a more mature demographic profile, with implications for everything from urban planning to economic policy. Understanding these dynamics is not just an academic exercise; it is crucial for policymakers, researchers, and anyone interested in the future trajectory of this influential nation. The challenges and opportunities presented by the evolving population in Iran—be it the need for job creation, sustainable urban development, or adapting to an aging society—will shape its path for decades to come. As Iran continues to navigate these complex demographic waters, its ability to harness its human capital and adapt to changing trends will be key to its continued development and influence on the global stage. We encourage you to share your thoughts on these demographic trends in the comments below or explore other articles on our site for more insights into global population dynamics.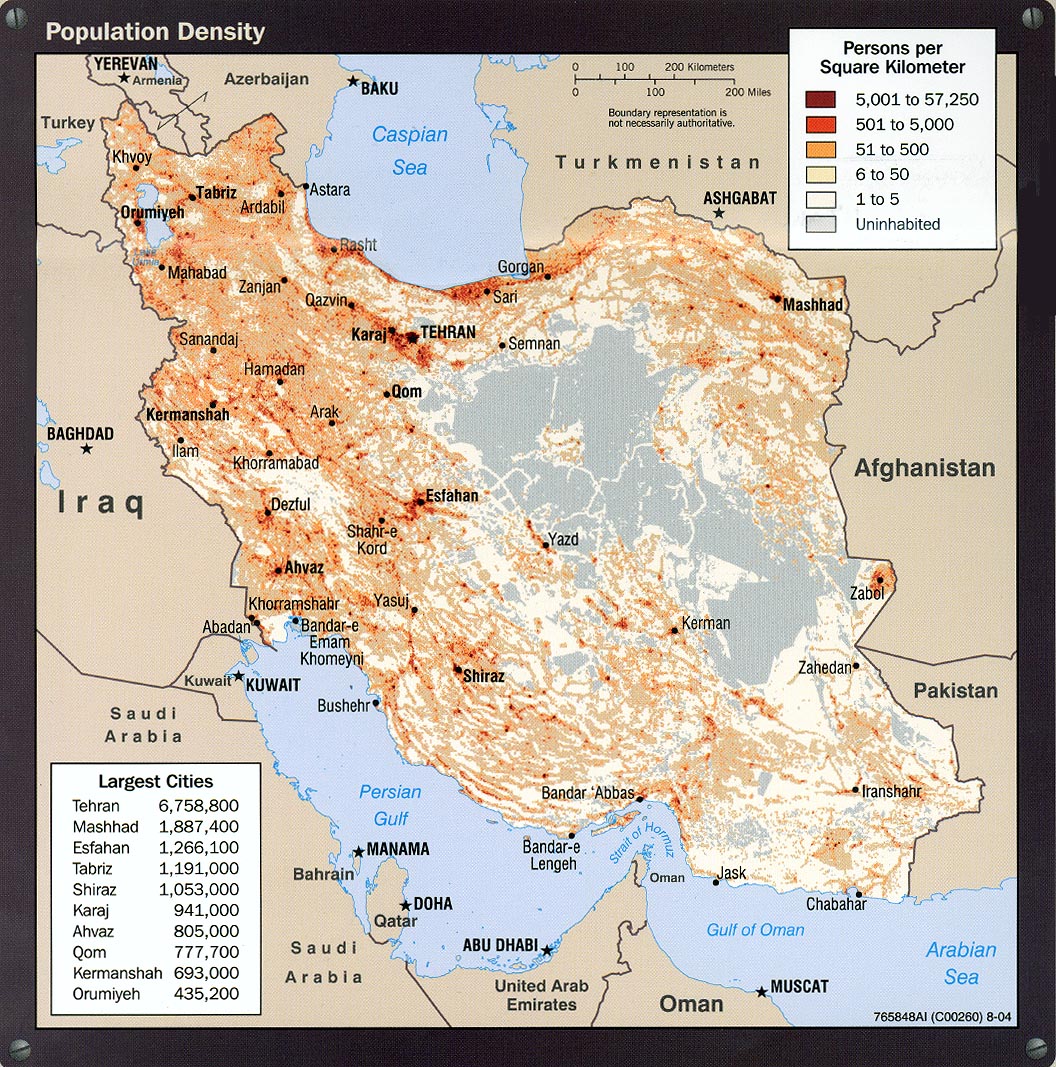
Iran Population Density Map - Iran • mappery

Population of Iran - Chronicle Fanack.com
Live Iran Population Clock 2025 - Polulation of Iran Today