Iran Vs Israel Military Power: A Deep Dive Into Their Strengths
The ongoing geopolitical tensions in the Middle East frequently bring the military capabilities of regional powers into sharp focus. Among these, the comparison of military strength between Iran and Israel stands out as a critical subject, drawing significant international attention. Understanding the nuances of their respective armed forces is essential for anyone seeking to comprehend the potential dynamics of a direct conflict in this volatile region. Both nations possess formidable military establishments, yet their strategic doctrines, technological advancements, and force compositions differ significantly, painting a complex picture of their true power balance. This article delves into a comprehensive analysis of their military might, drawing on the latest available data to shed light on who might hold the upper hand.
Recent escalations, including reported Israeli operations like "Operation Rising Lion" and Iran's subsequent responses, underscore the urgency of such an analysis. While direct large-scale confrontations have historically been avoided, the increasing frequency of indirect engagements and rhetorical exchanges necessitates a clear-eyed assessment of their military capabilities. This detailed examination aims to provide a clear and concise overview, helping to demystify the often-complex world of military comparisons between these two key players.
Table of Contents
- Overall Global Firepower Rankings: A Closer Look
- Personnel Strength: Quantity Versus Strategic Advantage
- Ground Forces: Tanks, Artillery, and Armored Vehicles
- Air Power: The Crucial Domain of Modern Warfare
- Naval Capabilities and Maritime Strategy
- Technological Edge and Nuclear Capabilities
- Military Expenditure and Sanctions Impact
- Proxy Warfare and Regional Influence
Overall Global Firepower Rankings: A Closer Look
When assessing the comparison of military strength between Iran and Israel, a good starting point is the Global Firepower Index (GFP). This widely recognized organization provides an annual statistical overview of military capabilities across various nations. According to Global Firepower (GFP) 2024 data, the military strength of Israel and Iran is not drastically different in terms of overall power. However, the specific rankings and PowerIndex (PwrIndx) scores offer a more nuanced picture. Based on data for 2025, Iran is positioned at rank 14 out of 145 countries, boasting a PwrIndx of 0.2269. In contrast, Israel is ranked 17th with a PwrIndx of 0.2596. It's crucial to remember that in the GFP ranking system, a lower PwrIndx score indicates greater military strength. Therefore, based on these specific 2025 figures, Iran is assessed as having a stronger military than Israel.
- Adam Harrison
- Hubflix Hindi
- Corde Broadus
- When Did Jennifer And Brad Divorce
- Brennan Elliott Wife Cancer
However, it's worth noting that other interpretations or earlier data points might present a slightly different view. For instance, some analyses from Global Firepower Index 2024 suggest Israel holds a slight edge over Iran in global military strength, reflecting the continually evolving strategic rivalry. This highlights the dynamic nature of these rankings, which are influenced by a multitude of factors, including ongoing military procurements, technological advancements, and geopolitical shifts. The subtle differences in these indices underscore the tight competition and the complex interplay of various military assets when comparing the military strength of Iran vs Israel.
Personnel Strength: Quantity Versus Strategic Advantage
One of the most immediate and striking differences in the comparison of military strength between Iran and Israel lies in their personnel numbers. Iran possesses a significant quantitative advantage in this domain, a factor that often plays a crucial role in sustained conflict scenarios, particularly those involving ground operations or prolonged engagements.
Iran's Numerical Superiority
Iran boasts a substantial active military force, comprising over 600,000 personnel. This impressive figure includes the regular army (Artesh), the Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps (IRGC), and the Basij paramilitary forces. The IRGC, in particular, is a powerful and ideologically driven branch, distinct from the regular army, with significant influence over Iran's strategic policies and external operations. When factoring in reservists, Iran's total personnel strength could potentially exceed 900,000. This vast pool of manpower provides Iran with considerable depth for defensive operations, as well as the potential for large-scale mobilization if required. The sheer volume of personnel could present a formidable challenge in any protracted conflict, allowing for sustained operations and the absorption of significant casualties, which is a key consideration when analyzing the military strength of Iran vs Israel.
Israel's Strategic and Technological Edge
While specific active personnel numbers for Israel are not provided in the reference data, it is widely understood that Israel operates with a significantly smaller active force compared to Iran. However, Israel compensates for this numerical disparity through a highly trained, technologically advanced, and well-equipped military, supported by a robust reserve system that can be rapidly mobilized. Israel's military doctrine emphasizes quality over quantity, leveraging superior technology, advanced training, and strategic intelligence to maintain a qualitative edge. Furthermore, Israel's mandatory conscription system ensures a large pool of well-trained reservists who can be quickly integrated into active units during times of crisis. This focus on technological superiority and rapid mobilization is a cornerstone of Israel's defense strategy, designed to overcome potential numerical disadvantages and ensure effective response capabilities against a larger adversary.
Ground Forces: Tanks, Artillery, and Armored Vehicles
The strength of ground forces is a critical component of any military comparison, especially when considering the potential for direct confrontation. The 'The Military Balance 2023' publication by IISS provides valuable insights into Iran's ground capabilities. According to this report, Iran possesses a substantial inventory of ground combat equipment, including approximately 10,513 main battle tanks, 6,798 artillery pieces, and over 640 armored personnel carriers (APCs). This vast collection of heavy armor and artillery indicates Iran's capacity for large-scale land operations and defensive postures, reflecting a traditional emphasis on conventional ground warfare capabilities. The sheer volume of these assets suggests a focus on mass and endurance in ground engagements, a significant aspect when evaluating the military strength of Iran vs Israel.
While the provided data does not offer specific comparable figures for Israel's ground forces, it is generally understood that Israel's armored and artillery units, though potentially smaller in raw numbers, are characterized by their advanced technology, superior maintenance, and high levels of operational readiness. Israel's Merkava tank series, for instance, is renowned for its advanced protection and firepower, representing a qualitative advantage. The Israel Defense Forces (IDF) also integrate sophisticated command and control systems, precision artillery, and advanced anti-tank capabilities to maximize the effectiveness of their ground units. Therefore, while Iran might boast a larger inventory, Israel's qualitative superiority in terms of technology and training would likely be a significant factor in any direct ground engagement, creating a complex dynamic in the overall comparison of military strength.
Air Power: The Crucial Domain of Modern Warfare
In any modern conflict, air superiority often dictates the pace and outcome of engagements. The comparison of military strength between Iran and Israel in the aerial domain reveals a stark contrast, with Israel holding a clear advantage in certain critical aspects, while Iran has developed alternative strategies to project power from the air.
Israel's Dominance in Aerial Assets
Israel possesses a significant quantitative advantage in combat aircraft and helicopters. Its air force is equipped with a modern fleet of fighter jets, including advanced F-16s and F-35s, which are among the most capable aircraft in the world. These aircraft provide Israel with superior air-to-air combat capabilities, precision strike potential, and robust air defense. The qualitative edge of Israel's air force is further amplified by its access to advanced avionics, electronic warfare systems, and sophisticated targeting pods, often supplied or developed in cooperation with the United States. This technological superiority allows Israel to project power effectively, conduct long-range strikes, and maintain air dominance over its operational areas. The ability to control the skies is a critical element of Israel's military doctrine, enabling it to neutralize threats before they reach its borders and to support ground operations with overwhelming firepower. This aspect significantly tips the scales in Israel's favor in the overall comparison of military strength.
Iran's Reliance on Missiles and Drones
In contrast, Iran's air force largely consists of older, Russian-made fighter jets, numbering around 180, which are considered outdated and face significant maintenance challenges due to international sanctions. These sanctions have severely hampered Iran's ability to acquire modern aircraft or even spare parts, forcing it to rely on domestic production and ingenuity for upkeep. Consequently, Iran has increasingly focused on developing and deploying a formidable arsenal of missiles and drones as a strategic alternative to its aging air force. Recent events, such as Iran's extensive barrage of over 300 projectiles (missiles and drones) towards Israel, demonstrate its capability to strike from long distances. This reliance on asymmetrical air power, particularly ballistic and cruise missiles, and a wide array of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), represents a key component of Iran's strategy to overcome its conventional air inferiority. These assets provide Iran with a significant long-range strike capability, posing a different kind of threat that is harder to counter than traditional air-to-air engagements, thereby adding a unique dimension to the military strength of Iran vs Israel.
Naval Capabilities and Maritime Strategy
While the provided data does not offer extensive details on the naval forces of both nations, maritime capabilities play an undeniable role in regional power projection and defense. Iran, with its extensive coastline along the Persian Gulf and the Gulf of Oman, places significant emphasis on its naval forces, particularly the IRGC Navy, which operates alongside the conventional Artesh Navy. Iran's naval strategy largely focuses on asymmetric warfare, utilizing a large number of fast attack crafts, submarines (including midget submarines), anti-ship missiles, and naval mines to control vital waterways like the Strait of Hormuz. Their doctrine aims to deny access to larger, more technologically advanced navies, rather than engaging in direct blue-water confrontations. This approach is designed to leverage geographical advantages and inflict disproportionate costs on an adversary, making it a crucial component in the overall military strength of Iran vs Israel.
Israel, on the other hand, operates a smaller but highly advanced navy, primarily focused on coastal defense, protecting its vital maritime trade routes, and conducting special operations. Its fleet includes advanced corvettes and submarines, some of which are believed to be nuclear-capable, providing a second-strike capability. Israel's naval assets are integrated with its broader defense network, benefiting from superior intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance (ISR) capabilities. While not designed for large-scale naval engagements in distant waters, Israel's navy is highly effective in its operational environment, capable of precision strikes and maintaining maritime security. The differing naval doctrines and operational environments mean that a direct comparison of naval strength is complex, with each nation optimizing its forces for distinct strategic objectives within the broader context of their military capabilities.
Technological Edge and Nuclear Capabilities
Beyond conventional forces, the technological sophistication and the presence of unconventional weapons significantly influence the perception and reality of military power. In this crucial aspect of the comparison of military strength, Israel holds a distinct and widely acknowledged advantage.
Israel possesses a well-established technological edge across its military, from advanced avionics and missile defense systems (like the Iron Dome and Arrow systems) to sophisticated cyber warfare capabilities and intelligence gathering. This superiority is a result of substantial investment in research and development, a thriving domestic defense industry, and strong strategic partnerships, particularly with the United States. This technological prowess allows Israel to maintain a qualitative advantage over its adversaries, enabling precision strikes, effective defense against incoming threats, and advanced battlefield awareness. Furthermore, Israel is widely believed to possess nuclear weapons, though it maintains a policy of deliberate ambiguity regarding its nuclear arsenal. This undeclared nuclear capability serves as a powerful deterrent, often referred to as its "last resort" option, significantly influencing the strategic calculus in the region and adding a profound layer to the military strength of Iran vs Israel.
Iran, conversely, does not possess nuclear weapons. According to a US Department of Defense intelligence report (DIA), Iran's capacity for uranium enrichment is limited, preventing it from producing nuclear weapons. Despite its robust missile program and advancements in drone technology, Iran faces significant challenges in matching Israel's overall technological sophistication, largely due to decades of international sanctions. These sanctions have restricted its access to advanced components, Western military technology, and cutting-edge research. Consequently, Iran has focused on developing indigenous capabilities, often through reverse engineering or acquiring technology from non-Western sources. While Iran has made strides in ballistic missile technology and drone production, its overall technological base remains behind Israel's, particularly in areas like precision guidance, stealth technology, and integrated air defense systems. This disparity in technological advancement and the presence of nuclear weapons represent a critical imbalance in the overall military power equation.
Military Expenditure and Sanctions Impact
Military expenditure is a direct indicator of a nation's investment in its defense capabilities, reflecting its ability to procure advanced weaponry, maintain its forces, and conduct research and development. In the comparison of military strength between Iran and Israel, significant disparities in military budgets are evident.
Israel consistently maintains a substantially larger military budget compared to Iran. This allows Israel to invest heavily in cutting-edge defense technologies, procure advanced aircraft and missile systems from international partners (primarily the United States), and ensure high levels of training and readiness for its personnel. The larger budget also supports Israel's robust defense industry, which is a global leader in various military technologies, contributing to its qualitative edge. This financial capacity is a key enabler of Israel's technological superiority and its ability to maintain a modern and highly effective fighting force.
Iran, on the other hand, operates under severe international sanctions, which have profoundly impacted its military budget and procurement capabilities. These sanctions have restricted its access to global financial markets, advanced military hardware, and even spare parts for its existing equipment. As a result, Iran has been forced to rely heavily on indigenous production, reverse engineering, and the development of asymmetric capabilities like missiles and drones, which are cheaper to produce and deploy. While Iran's military budget is substantial within its regional context, it pales in comparison to Israel's, especially when considering purchasing power and access to high-end military technology. The long-term impact of sanctions means that Iran's military modernization efforts are significantly constrained, forcing it to innovate within limitations. This economic disparity is a crucial factor shaping the overall military strength of Iran vs Israel, influencing everything from equipment quality to operational readiness.
Proxy Warfare and Regional Influence
The military strength of Iran vs Israel cannot be fully understood without considering their extensive engagement in proxy warfare and their broader regional influence. Both nations employ strategies that extend beyond direct military confrontation, leveraging alliances, supporting non-state actors, and engaging in covert operations to advance their strategic interests and undermine their adversaries.
Iran has cultivated a vast network of proxies and allied groups across the Middle East, often referred to as the "Axis of Resistance." These include powerful entities like Hezbollah in Lebanon, various Shiite militias in Iraq, Houthi rebels in Yemen, and to some extent, Hamas and Palestinian Islamic Jihad in Gaza. Iran provides these groups with financial support, training, and weaponry, including missiles and drones, enabling them to exert influence and pose threats to Israel and its allies. The recent escalation, including Hezbollah launching a series of combat drone and rocket attacks into northern Israel, exemplifies this strategy. This proxy network allows Iran to project power and engage in low-intensity conflict without directly committing its own forces, creating a complex web of regional security challenges for Israel.
Israel, in response, also engages in covert operations, intelligence gathering, and targeted strikes against Iranian assets and proxies across the region. Reports of Israeli airstrikes in Syria against Iranian-backed militias and weapons convoys are common, as are alleged cyberattacks and assassinations of Iranian nuclear scientists. Israel's strategy aims to degrade Iran's capabilities, disrupt its supply lines to proxies, and deter further aggression. The ongoing "shadow war" involves sophisticated intelligence operations, cyber warfare, and targeted military actions, reflecting a highly dynamic and often undeclared conflict. This aspect of proxy warfare and regional influence adds another layer of complexity to the comparison of military strength, demonstrating that military power is not solely about conventional forces but also about the ability to shape the regional security landscape through indirect means.
Conclusion
The comparison of military strength between Iran and Israel reveals a multifaceted and highly complex dynamic, where each nation possesses distinct advantages and vulnerabilities. While Iran demonstrates a significant quantitative superiority in terms of active personnel and certain ground assets, its military is largely constrained by an aging air force and the enduring impact of international sanctions. Conversely, Israel, despite its smaller size, boasts a qualitative edge rooted in advanced technology, a modern air force, and a highly trained military, complemented by a formidable, albeit undeclared, nuclear deterrent.
The Global Firepower Index 2025 suggests Iran holds a slightly higher overall ranking, yet this must be weighed against Israel's undeniable technological and strategic advantages, particularly in air power, intelligence, and precision strike capabilities. The increasing reliance of Iran on missile and drone technology as an asymmetric response to its conventional limitations, coupled with its extensive network of regional proxies, further complicates the power balance. Recent direct exchanges, such as Iran's large-scale projectile attack and Israel's retaliatory strikes, underscore the volatile nature of their rivalry and the potential for rapid escalation.
Ultimately, a direct military confrontation would likely be devastating for both sides, involving a complex interplay of conventional forces, asymmetric warfare, and potentially long-range strikes. The true military strength of Iran vs Israel is not merely a matter of numbers or rankings but a delicate balance of capabilities, strategic doctrines, and geopolitical alliances. Understanding these intricate layers is vital for grasping the security challenges in the Middle East. We encourage you to share your thoughts on this complex topic in the comments below, and explore our other articles for more in-depth analyses of regional security dynamics.

IRAN

IRAN
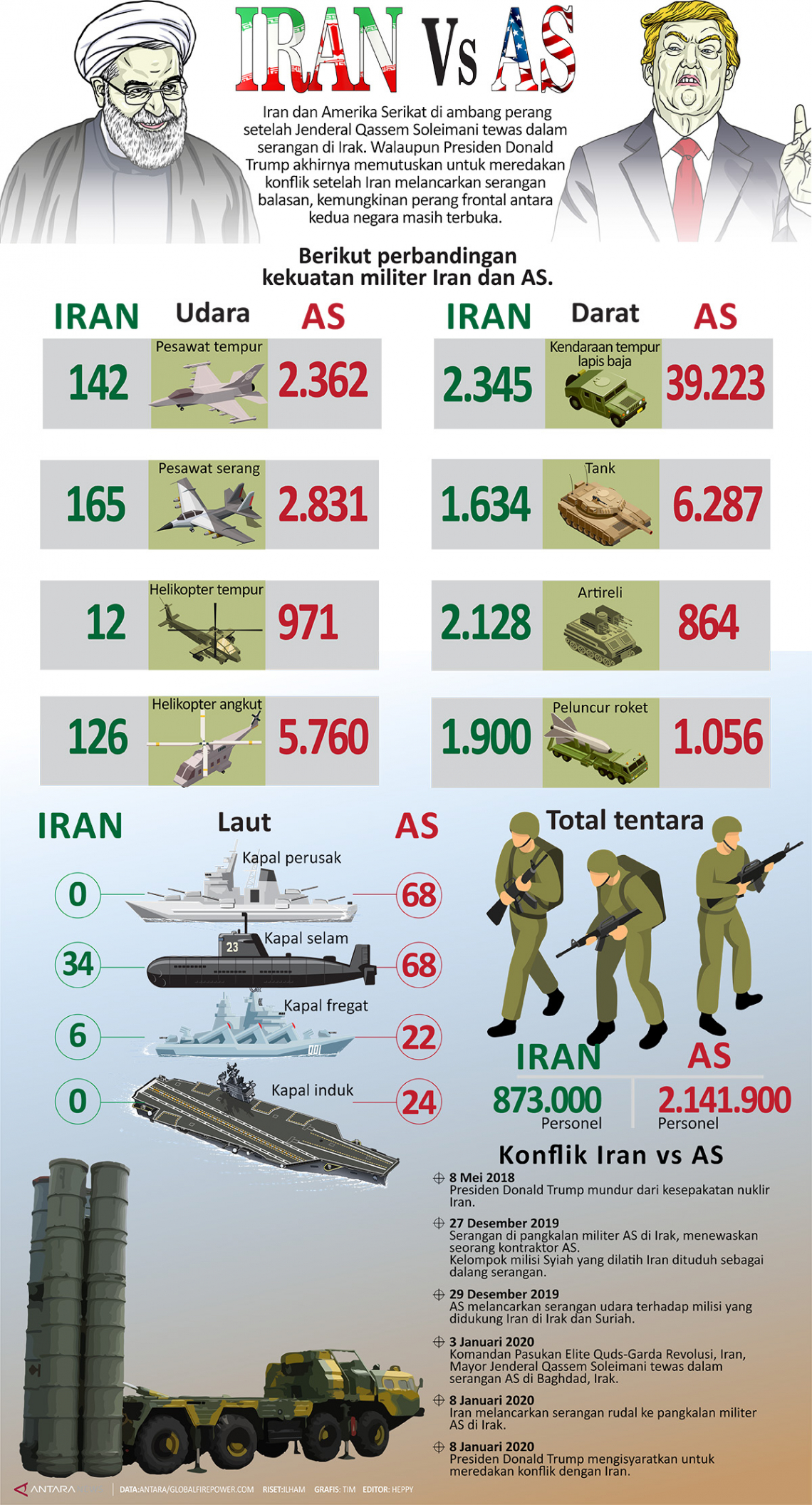
Kekuatan militer Iran vs AS - Infografik ANTARA News