Iran Vs Israel Population: Unpacking The Demographic Divide
In the complex tapestry of the Middle East, the relationship between Iran and Israel stands as one of the most significant and often volatile geopolitical dynamics. While military might and political ideologies frequently dominate headlines, understanding the fundamental demographic realities – specifically, the stark differences in Iran vs Israel population – is crucial for a comprehensive grasp of their respective strengths, vulnerabilities, and strategic postures. This article delves deep into the demographic landscape of both nations, exploring how population size, growth, and composition shape their military capabilities, economic potential, and overall societal dynamics.
Beyond mere numbers, the demographic profiles of Iran and Israel tell a story of distinct historical trajectories, societal structures, and future challenges. From the rapid population growth experienced by Israel since its admission to the UN in 1949, fueled by waves of migration, to Iran's enduring large populace, shaped by its own unique history including the devastating Iran-Iraq War of the 1980s, these demographic realities underpin much of their ongoing rivalry. By examining these core statistics and their broader implications, we can gain a clearer perspective on the inherent asymmetries that define the Iran vs Israel population dynamic.
Table of Contents
- Iran vs Israel Population: A Demographic Overview
- Historical Demographic Trajectories
- Geographical and Political Contexts
- Military Manpower: A Numbers Game
- Economic Implications of Population Size
- Societal Dynamics and Population Growth Rates
- The Shifting Geopolitical Landscape
- Conclusion: Demographics as a Foundational Factor
Iran vs Israel Population: A Demographic Overview
At the heart of any comparison between Iran and Israel lies a fundamental demographic disparity. The sheer scale of Iran's population dwarfs that of Israel, creating a significant asymmetry in terms of human resources. According to 2023 estimates, Israel's population is a little over 9.4 million. In stark contrast, Iran has nearly 10 times more than that. More specifically, recent data from Global Firepower's 2024 index indicates Iran’s population stood at 87,590,873. Another reference points to Iran having a population of 88.3 million. Earlier figures also cited Iran's population at 74,798,599 compared to Israel’s 7,765,700, underscoring a consistent trend of Iran possessing a much larger populace. This substantial difference in the Iran vs Israel population is not merely an interesting statistic; it has profound implications across various domains, from military capabilities to economic potential and societal resilience. The land area also highlights this disparity: Israel is approximately 21,937 sq km, while Iran is approximately 1,648,195 sq km, making Iran 7,413% larger than Israel. This vast geographical expanse, coupled with a much larger population, inherently grants Iran a different strategic depth and resource base compared to its smaller, more densely populated counterpart. The difference in population size is arguably one of the most defining characteristics when assessing the overall might and strategic outlook of these two nations.Historical Demographic Trajectories
The current demographic landscape of both Iran and Israel is a product of their unique historical journeys, marked by significant events that have shaped their population growth and composition. Understanding these trajectories is essential to grasping the current Iran vs Israel population dynamic.Israel's Population Boom
Israel's demographic story is one of rapid and deliberate growth. Israel was admitted as a member of the UN in 1949 and saw rapid population growth, primarily due to migration from Europe and the Middle East over the following years. This influx of Jewish immigrants, often fleeing persecution or seeking to fulfill Zionist aspirations, dramatically swelled the nascent nation's numbers. This initial wave laid the foundation for a country that, despite its small geographical size, has managed to maintain a relatively high birth rate compared to many Western nations. The continuous, albeit fluctuating, immigration has remained a key factor in its demographic expansion. Despite facing numerous external threats, Israel has maintained a resilient population growth. The nation fought wars against its Arab neighbors in 1967 and 1973, followed by peace treaties with Egypt in 1979 and Jordan in 1994. These conflicts and subsequent periods of peace have all, in their own ways, influenced migration patterns and internal demographic shifts, yet the overall trend has been one of consistent, albeit sometimes challenging, population increase.Iran's Resilience and Growth
Iran's population history is characterized by its ancient roots and, more recently, by periods of significant upheaval. For most of the 1980s, Iran fought a war with Iraq that resulted in millions of casualties and economic devastation for both sides. This devastating conflict undoubtedly impacted Iran's demographic trajectory, leading to a generation marked by loss and hardship. However, despite such immense challenges, Iran's population has continued to grow, maintaining its status as a populous nation in the region. The average population growth rate reflects the annual increase or decrease in population. Currently, the world’s population is growing at a rate of approximately 1.07% per year. While specific current growth rates for Iran are not provided, its large base population ensures that even moderate growth rates translate into substantial absolute increases in numbers. The higher the growth, the more dynamic society feels, and this dynamism, combined with its historical resilience, contributes to Iran's perception of strength in numbers.Geographical and Political Contexts
The demographic comparison of Iran vs Israel population cannot be fully appreciated without considering their respective geographical footprints and political systems. These factors profoundly influence how population figures translate into national power and strategic posture. Geographically, Iran is approximately 1,648,195 sq km, making it a vast country with diverse landscapes and significant natural resources. Israel, by contrast, is approximately 21,937 sq km, a tiny sliver of land in comparison. This immense size difference means Iran has greater strategic depth, more dispersed population centers, and a wider array of geographical features that can be leveraged for defense or resource extraction. For Israel, its small size necessitates a different strategic approach, often relying on technological superiority and rapid response capabilities. Politically, the two nations operate under vastly different systems. Israel is a parliamentary democracy, meaning that the parliament and the country are governed democratically through elections, and that the head of state is usually a ceremonial figure, with real power vested in the prime minister and the Knesset. This democratic framework, despite its internal complexities, generally allows for a more open society and a system where public opinion can directly influence policy. Iran, on the other hand, is governed as a unitary state and is an Islamic Republic. Iran's political system has elements of a presidential democracy with a theocracy governed by an autocratic supreme leader. This unique blend of elected officials and unelected clerical authority shapes its domestic policies, its approach to international relations, and how it mobilizes its population and resources. The ideological underpinnings of the Islamic Republic are a defining feature of its state apparatus and its foreign policy, often putting it at odds with Western democracies and regional rivals like Israel. These differing political systems also influence how each state views its population – as citizens with rights in a democracy, or as a populace guided by religious and revolutionary principles in a theocracy.Military Manpower: A Numbers Game
When assessing the "Might of Iran vs Israel," the discussion inevitably turns to military capabilities, where the Iran vs Israel population disparity plays a critical role, particularly in terms of available manpower. A larger population generally translates to a larger pool of potential soldiers, which is a significant factor in conventional warfare scenarios.Iran's Vast Pool of Potential Soldiers
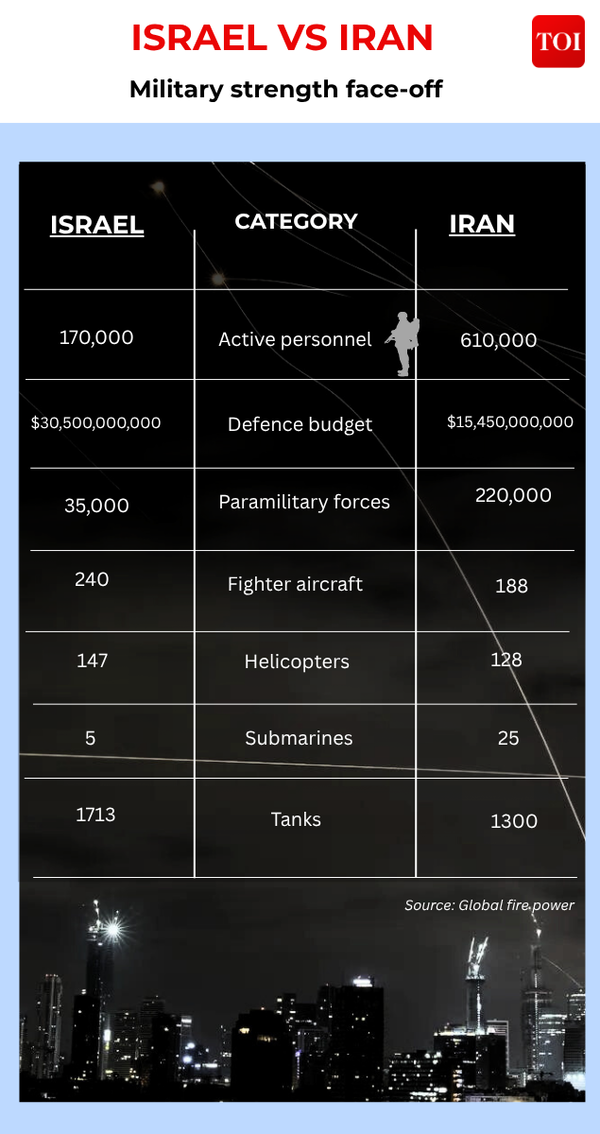
Iran has a population ten times larger than Israel’s, from which it draws its armed forces. This substantial population size translates into a larger pool of available manpower for Iran, with 49.05 million individuals fit for service, compared to Israel’s 3.80 million. When considering those fit for service, Iran maintains a substantial lead with 41.17 million individuals, outpacing Israel’s 3.16 million. Another data point indicates that Iran has access to a population of 41.1 million who are considered fit for service, while by comparison, Israel’s population offers a much smaller pool of potential soldiers — about 3.15 million. Despite this vast pool, Iran maintains a much larger standing force. In addition to its 610,000 active troops, Iran's ability to mobilize a significant portion of its population for military service or support functions gives it a quantitative advantage that few regional powers can match. This sheer numerical superiority in potential and active personnel is a cornerstone of Iran's defense doctrine, emphasizing mass and resilience.Israel's Smaller but Battle-Hardened Force
For a small nation, Israel also has a considerable supply of troops, with about 170,000 active duty forces and another 400,000 reserves. While these numbers are significantly fewer than Iran’s, Israel’s forces have been battle-hardened by regional conflicts. This extensive combat experience, combined with advanced military technology and a highly trained professional army, allows Israel to punch above its weight class. The quality of training, technological superiority, and strategic doctrine often compensate for numerical disadvantages. Israel's mandatory conscription for both men and women, coupled with a robust reserve system, ensures that a large percentage of its adult population has military training and can be rapidly mobilized in times of crisis. This high level of readiness and experience is a critical factor in understanding Israel's military capabilities, even with a much smaller Iran vs Israel population comparison.Economic Implications of Population Size
The size and composition of a nation's population are intrinsically linked to its economic potential and challenges. While the provided data offers specific figures like "404,626 m us$" and "513,611 m us$" which likely refer to Gross National Product (GNP) or GDP for the respective countries, and "4.47 m us$" and "52.64 m us$" for per capita figures (though specific attribution is not provided in the data), the general principle holds: a larger population can mean a larger workforce and consumer base, but also greater demands on resources and infrastructure. For Iran, its massive population presents both an opportunity and a challenge. A large workforce can drive industrial output and innovation, provided there are sufficient jobs and educational opportunities. However, it also means a greater need for employment, housing, food, and social services. Managing such a large population requires robust economic planning and resource allocation, especially under international sanctions that have historically impacted Iran's economy. The Iran-Iraq war of the 1980s, which resulted in economic devastation for both sides, further illustrates how external conflicts can profoundly impact a nation's ability to leverage its human capital for economic growth. Israel, with its much smaller population, has adopted a different economic model, focusing on high-tech industries, innovation, and knowledge-based services. Its smaller workforce is highly skilled and educated, contributing to a vibrant startup ecosystem often dubbed "Startup Nation." While it doesn't have the sheer manpower for large-scale, labor-intensive industries like Iran, its economic strength lies in its human capital quality and technological prowess. The economic figures, even without clear attribution, hint at significant economic activity in both nations, but their paths to economic development are shaped by their demographic realities.Societal Dynamics and Population Growth Rates
Population growth rates and the average age of a population significantly influence societal dynamics, including social stability, innovation, and long-term planning. The average population growth rate reflects the annual increase or decrease in population. Currently, the world’s population is growing at a rate of approximately 1.07% per year. The higher the growth, the more dynamic society feels. For Iran, a large and potentially young population can be a double-edged sword. A youthful demographic can provide a dynamic workforce and a large consumer market, fostering economic growth and innovation. However, it also places immense pressure on educational systems, job markets, and social infrastructure. High youth unemployment, if not addressed, can lead to social unrest and instability. The political system of Iran, with its elements of a presidential democracy intertwined with a theocracy governed by an autocratic supreme leader, must navigate these demographic pressures while maintaining stability. Israel's population growth, historically driven by migration, has created a diverse society. The influx of people from various cultural backgrounds has enriched its social fabric but also presented challenges in terms of integration and national identity. The relatively high birth rates among certain segments of its population also contribute to its continued growth, ensuring a youthful demographic that can support its military and economic needs. Both nations, despite their vast differences in Iran vs Israel population, must contend with the evolving needs and aspirations of their respective populations.The Shifting Geopolitical Landscape
The demographic realities of Iran and Israel are not static; they are deeply intertwined with the evolving geopolitical landscape of the Middle East. The rivalry between these two nations is a central feature of regional politics, and their population dynamics play a role in their strategic calculations. Historically, Israel’s old periphery alliance with the Shah flipped after 1979, following the Iranian Revolution. This pivotal event transformed Iran from a regional partner to a staunch ideological adversary. Today, the two states back competing blocs: Iran’s "axis of resistance" versus Israel. This ideological and strategic competition manifests in various forms, including proxy conflicts, cyber warfare, and direct threats. Recent escalations underscore the volatile nature of this rivalry. Israel initiated an air campaign against Iran's nuclear and military facilities, leading to a conflict that escalated with Iran retaliating against Israeli targets. The involvement of global powers, such as President Donald Trump threatening Iran, further complicates the regional security environment. In this high-stakes environment, the fundamental demographic difference in Iran vs Israel population influences perceptions of power, resilience, and the capacity for sustained conflict. While Israel relies on qualitative advantages and strategic alliances, Iran leverages its numerical strength and strategic depth.Conclusion: Demographics as a Foundational Factor
In conclusion, the comparison between Iran and Israel reveals a complex interplay of demographic, financial, and military factors that shape their respective defense postures. The sheer scale of Iran's population, which is approximately ten times larger than Israel's, provides it with a vast pool of human resources, translating into a significantly larger potential and active military force. This numerical superiority is a key component of Iran's strategic thinking, enabling it to project power through mass and resilience. Conversely, Israel, despite its much smaller population, compensates through technological superiority, a highly trained and battle-hardened military, and a robust reserve system. Its rapid population growth post-1949, driven by migration, has sustained its human capital, while its focus on high-tech industries has propelled its economic development. The historical trajectories, political systems, and ongoing geopolitical tensions further underscore how these demographic realities influence the strategic calculus of both nations. Understanding the profound differences in Iran vs Israel population is not just an academic exercise; it is essential for comprehending the dynamics of one of the world's most critical geopolitical rivalries. These demographic disparities are foundational to their military capabilities, economic potential, and societal structures, shaping their past, present, and future interactions. We hope this in-depth analysis has provided valuable insights into the demographic realities underpinning the Iran-Israel dynamic. What are your thoughts on how population differences influence international relations? Share your perspectives in the comments below, or explore more of our articles on geopolitical analyses and demographic trends to deepen your understanding of global affairs.
Israel Vs Iran - Brilliant Maps

Iran is too weak to wage a ground war against Israel - The Spectator World
The Ayatollah’s gamble: Fight, fold, or fall - How far will Iran go